Published online by Cambridge University Press: 11 April 2019
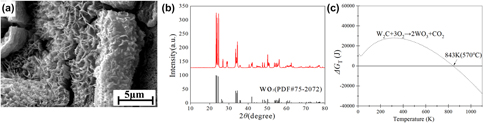
Cast tungsten carbide is widely used to reinforce iron or steel substrate surface composites to meet the demands of harsh wear environments due to its extremely high hardness and excellent wettability with molten steel. Cast tungsten carbide particle/steel matrix surface composites have demonstrated great potential development in applications under the abrasive working condition. The thermal shock test was used to investigate the fatigue behavior of the composites fabricated by vacuum evaporative pattern casting technique at different temperatures. At elevated temperatures, the fatigue behavior of the composites was influenced by the oxidation of tungsten carbide, producing WO3. Thermodynamic calculations showed that the W2C in the tungsten carbide particle was oxidized at an initial temperature of approximately 570 °C. The relationship between oxidation and thermal fatigue crack growth was investigated, and the results suggested that oxidation would become more significant with increasing thermal shock temperature. These findings provide a valuable guide for understanding and designing particle/steel substrate surface composites.