Published online by Cambridge University Press: 07 February 2020
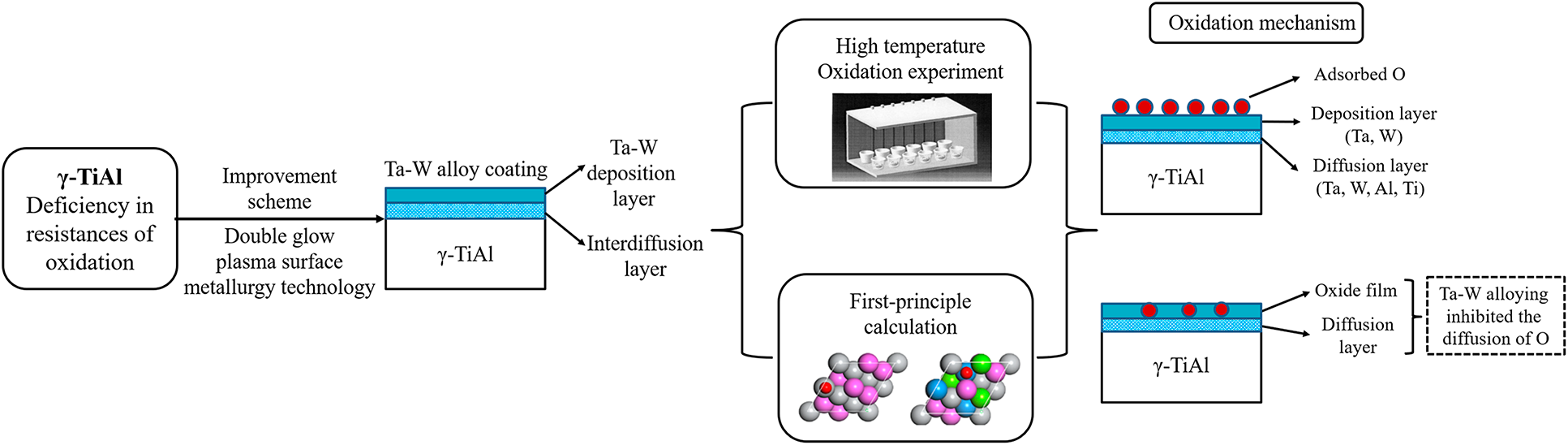
Ta–W co-alloying was realized by double glow plasma surface metallurgy technology, and their effects on high-temperature oxidation behavior of γ-TiAl were studied. Ta–W co-alloying coating was composed of a deposited layer and interdiffusion layer. The results of isothermal oxidation experiment indicated that a compact mixed oxide film of Ta and W was formed on the sample. The interdiffusion layer reduced the oxygen intrusion that improved the high-temperature oxidation resistance of γ-TiAl. The effects of Ta–W co-alloying on oxygen adsorption energy and electronic structure of γ-TiAl(111) were analyzed by first-principle calculation. The results showed that the optimal adsorption sites of O atoms changed from fcc-Al to hcp-Ti and hcp-Al, indicating that Ta–W co-alloying inhibited the diffusion of O. The electronic structure analysis of γ-TiAl(111) after Ta–W alloying indicated the affinity of Ti and O was inhibited, which resulted in decreased TiO2 in the oxide film.