Published online by Cambridge University Press: 11 February 2013
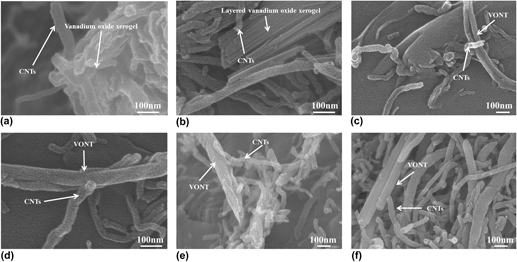
Vanadium oxide nanorods (VONRs) and vanadium oxide nanotubes (VONTs) were fabricated by hydrothermal method with the induction of hydroxyl and carboxyl functionalized carbon nanotubes (CNTs). The functionalized CNTs not only facilitate the dispersion of CNTs but also serve as centers for polymerization in the hydrothermal reaction. The formation of (VONRs) and (VONTs) was observed by field emission scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, x-ray powder diffraction and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy tests. Self-assembling nanotubes and nanorods were formed together with the layered structures, but they followed different formation mechanisms. The “Rolling” and “Attaching-Oriented Attachment Growth” mechanisms are proposed to describe the formation of VONRs and VONTs, respectively.