Published online by Cambridge University Press: 10 February 2015
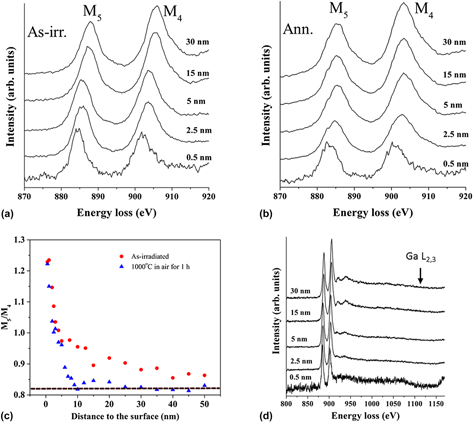
A systematic x-ray diffraction (XRD) study was performed on room-temperature Xe-irradiated and postirradiation annealed CeO2. Large scale XRD did not show any additional irradiation-induced phases upon irradiation. Depth profiling the CeO2 (111) diffraction peak over the 150 nm deep Xe-irradiated layer (400 keV, 1 × 1020 Xe/m2) by grazing incidence XRD indicated a lattice expansion at the irradiated layer. Postirradiation annealing (1 h at 1000 °C) in an oxygen-containing environment removed the observed XRD features. Electron energy loss spectroscopy (EELS) was performed for cross-sectional samples before and after postirradiation annealing. EELS showed that the Ce charge state changed from +4 to +3 at the CeO2 surface indicating the presence of O vacancies in both as-irradiated and annealed samples. EELS also indicated that the amount of O vacancies was reduced at the irradiated region by annealing. The experimental results are discussed based on electronic properties of CeO2, annihilation of oxygen vacancies, and evolution of irradiation damage.
Contributing Editor: Khalid Hattar