Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Abu-Madi, M.A.
Lewis, J.W.
Mikhail, M.
El-Nagger, M.E.
and
Behnke, J.M.
2001.
Monospecific helminth and arthropod infections in an urban population of brown rats from Doha, Qatar.
Journal of Helminthology,
Vol. 75,
Issue. 4,
p.
313.
Abu-Madi, M.A.
Lewis, J.W.
Mikhail, M.
El-Nagger, M.E.
and
Behnke, J.M.
2001.
Monospecific helminth and arthropod infections in an urban population of brown rats from Doha, Qatar.
Journal of Helminthology,
Vol. 75,
Issue. 4,
p.
313.
Abu-Madi, M.A.
Behnke, J.M.
Mikhail, M.
Lewis, J.W.
and
Al-Kaabi, M.L.
2005.
Parasite populations in the brown rat Rattus norvegicus from Doha, Qatar between years: the effect of host age, sex and density.
Journal of Helminthology,
Vol. 79,
Issue. 2,
p.
105.
SINGLA, Lachhman D.
SINGLA, Neena
PARSHAD, Vir R.
JUYAL, Prayag D.
and
SOOD, Naresh K.
2008.
Rodents as reservoirs of parasites in India.
Integrative Zoology,
Vol. 3,
Issue. 1,
p.
21.
Mohd Zain, Siti N
Behnke, Jerzy M
and
Lewis, John W
2012.
Helminth communities from two urban rat populations in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia.
Parasites & Vectors,
Vol. 5,
Issue. 1,
Feliu, Carlos
López, Mercedes
Gómez, María
Torres, Jordi
Sánchez, Santiago
Miquel, Jordi
Abreu-Acosta, Néstor
Segovia, Juan
Martín-Alonso, Aarón
Montoliu, Isabel
Villa, Mercedes
Fernández-Álvarez, Ángela
Bakhoum, Abdoulaye
Valladares, Basilio
Orós, Jorge
and
Foronda, Pilar
2012.
Parasite fauna of rodents (Murinae) from El Hierro (Canary Islands, Spain): a multidisciplinary approach.
Acta Parasitologica,
Vol. 57,
Issue. 2,
Ribas, Alexis
López, Sergi
Makundi, Rhodes H.
Leirs, Herwig
and
de Bellocq, Joëlle Goüy
2013.
Trichuris spp. (Nematoda: Trichuridae) from Two Rodents, Mastomys natalensis and Gerbilliscus vicinus in Tanzania.
Journal of Parasitology,
Vol. 99,
Issue. 5,
p.
868.
Hancke, D.
and
Suárez, O.V.
2016.
Infection levels of the cestodeHymenolepis diminutain rat populations from Buenos Aires, Argentina.
Journal of Helminthology,
Vol. 90,
Issue. 2,
p.
199.
Archer, Colleen E
Appleton, Christopher C
Mukaratirwa, Samson
Lamb, Jennifer
and
Corrie Schoeman, M
2017.
Endo-parasites of public-health importance recovered from rodents in the Durban metropolitan area, South Africa.
Southern African Journal of Infectious Diseases,
Vol. 32,
Issue. 2,
p.
57.
Iliev, Petar T.
Georgiev, Georgi Zh.
Kirkova, Zvezdelina T.
and
Chakarova, Borislava G.
2017.
A Survey of Helminth Infections in the Black Rat from Stara Zagora District, Bulgaria.
Macedonian Veterinary Review,
Vol. 40,
Issue. 2,
p.
177.
Oguntomole, Oluwaseun
Nwaeze, Ugochukwu
and
Eremeeva, Marina
2018.
Tick-, Flea-, and Louse-Borne Diseases of Public Health and Veterinary Significance in Nigeria.
Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease,
Vol. 3,
Issue. 1,
p.
3.
Fitte, B.
Robles, M.R.
Dellarupe, A.
Unzaga, J.M.
and
Navone, G.T.
2018.
Hymenolepis diminuta and Rodentolepis nana (Hymenolepididae: Cyclophyllidea) in urban rodents of Gran La Plata: association with socio-environmental conditions.
Journal of Helminthology,
Vol. 92,
Issue. 5,
p.
549.
Isaac, Clement
Igbinosa, Benjamin Igho
Ohiolei, John Asekhaen
and
Osimen, Catherine Eki
2018.
Endoparasites of Small Mammals in Edo State, Nigeria: Public Health Implications.
The Korean Journal of Parasitology,
Vol. 56,
Issue. 1,
p.
93.
Zhu, Guang-Li
Tang, Yi-Yang
Limpanont, Yanin
Wu, Zhong-Dao
Li, Jian
and
Lv, Zhi-Yue
2019.
Zoonotic parasites carried by invasive alien species in China.
Infectious Diseases of Poverty,
Vol. 8,
Issue. 1,
Tijjani, Mustapha
Majid, Roslaini Abd
Abdullahi, Sharif Alhassan
and
Unyah, Ngah Zasmy
2020.
Detection of rodent-borne parasitic pathogens of wild rats in Serdang, Selangor, Malaysia: A potential threat to human health.
International Journal for Parasitology: Parasites and Wildlife,
Vol. 11,
Issue. ,
p.
174.
Kiene, Frederik
Andriatsitohaina, Bertrand
Ramsay, Malcolm S.
Rakotondramanana, Herinjatovo
Rakotondravony, Romule
Radespiel, Ute
and
Strube, Christina
2020.
Forest edges affect ectoparasite infestation patterns of small mammalian hosts in fragmented forests in Madagascar.
International Journal for Parasitology,
Vol. 50,
Issue. 4,
p.
299.
Herawati, Nur ‘Aini
Sudarmaji
Nugroho, W.S.
Widayanti, R.
Haryanto, A.
Widiasih, D.A.
Wijayanti, A.D.
Nugraha Setyawan, E.M.
Budiariati, V.
Anggita, M.
Choiriyah, E.
and
Arif, M.
2021.
Diversity of Rodent Species and Its Potency as the Vector for Transmitting Rodent Borne Parasitic Disease in Households.
BIO Web of Conferences,
Vol. 33,
Issue. ,
p.
07004.
Amaechi, E. C.
Ade-Akanbi, P. A.
Olagunju, I. T.
Okorie, C. A.
and
Ejike, B. U.
2021.
Occurrence and Prevalence of Macroparasites of African Giant Rats (Cricetomys Gambianus) in a Savanna Region of Nigeria.
Folia Veterinaria,
Vol. 65,
Issue. 2,
p.
36.
Bimi, Langbong
Yeboah, Joanita Asirifi
Adongo, Lucas Awane
Ofori, Benjamin Yeboah
Oduro, Daniel
Tetteh, Ato Kwamena
and
Owusu, Erasmus Henaku
2021.
Gastrointestinal parasites of three peri-domestic animals in selected areas in Accra, Ghana.
The Journal of Basic and Applied Zoology,
Vol. 82,
Issue. 1,
Khan, W.
Nisa, N. N.
Pervez, S.
Ahmed, S.
Ahmed, M. S.
Alfarraj, S.
Ali, A.
and
Tahreem, S.
2022.
Occurrence of Hymenolepis diminuta: a potential helminth of zoonotic importance in murid rodents.
Brazilian Journal of Biology,
Vol. 82,
Issue. ,
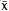 = 7.4 ± 0.74). Considering the rat-man proximity, this finding has considerable public health implications.
= 7.4 ± 0.74). Considering the rat-man proximity, this finding has considerable public health implications.