Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Deike, Luc
Popinet, Stephane
and
Melville, W. Kendall
2015.
Capillary effects on wave breaking.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 769,
Issue. ,
p.
541.
Melville, W. Kendall
and
Fedorov, Alexey V.
2015.
The equilibrium dynamics and statistics of gravity–capillary waves.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 767,
Issue. ,
p.
449.
Sutherland, Peter
and
Melville, W. Kendall
2015.
Measuring Turbulent Kinetic Energy Dissipation at a Wavy Sea Surface.
Journal of Atmospheric and Oceanic Technology,
Vol. 32,
Issue. 8,
p.
1498.
Malarkey, J.
and
Thorpe, S. A.
2016.
Line Vortices and the Vacillation of Langmuir Circulation.
Journal of Physical Oceanography,
Vol. 46,
Issue. 7,
p.
2123.
Saincher, Shaswat
and
Banerjee, Jyotirmay
2016.
Influence of wave breaking on the hydrodynamics of wave energy converters: A review.
Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews,
Vol. 58,
Issue. ,
p.
704.
Scully, Malcolm E.
Trowbridge, John H.
and
Fisher, Alexander W.
2016.
Observations of the Transfer of Energy and Momentum to the Oceanic Surface Boundary Layer beneath Breaking Waves.
Journal of Physical Oceanography,
Vol. 46,
Issue. 6,
p.
1823.
Deike, Luc
Melville, W. Kendall
and
Popinet, Stéphane
2016.
Air entrainment and bubble statistics in breaking waves.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 801,
Issue. ,
p.
91.
Pizzo, N. E.
and
Melville, W. Kendall
2016.
Wave modulation: the geometry, kinematics, and dynamics of surface-wave packets.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 803,
Issue. ,
p.
292.
Pizzo, N. E.
Deike, Luc
and
Melville, W. Kendall
2016.
Current generation by deep-water breaking waves.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 803,
Issue. ,
p.
275.
Derakhti, Morteza
Kirby, James T.
Shi, Fengyan
and
Ma, Gangfeng
2016.
Wave breaking in the surf zone and deep-water in a non-hydrostatic RANS model. Part 2: Turbulence and mean circulation.
Ocean Modelling,
Vol. 107,
Issue. ,
p.
139.
Pizzo, Nick E.
2017.
Surfing surface gravity waves.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 823,
Issue. ,
p.
316.
Deike, Luc
Pizzo, Nick
and
Melville, W. Kendall
2017.
Lagrangian transport by breaking surface waves.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 829,
Issue. ,
p.
364.
Lenain, Luc
and
Melville, W. Kendall
2017.
Evidence of Sea-State Dependence of Aerosol Concentration in the Marine Atmospheric Boundary Layer.
Journal of Physical Oceanography,
Vol. 47,
Issue. 1,
p.
69.
Sinha, Nityanand
and
Golshan, Roozbeh
2018.
Material Transport under a Wave Train in Interaction with Constant Wind: A Eulerian RANS Approach Combined with a Lagrangian Particle Dispersion Model.
Fluids,
Vol. 3,
Issue. 2,
p.
40.
Zippel, Seth F.
Thomson, Jim
and
Farquharson, Gordon
2018.
Turbulence from Breaking Surface Waves at a River Mouth.
Journal of Physical Oceanography,
Vol. 48,
Issue. 2,
p.
435.
De Vita, Francesco
Verzicco, Roberto
and
Iafrati, Alessandro
2018.
Breaking of modulated wave groups: kinematics and energy dissipation processes.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 855,
Issue. ,
p.
267.
Thorpe, S. A.
2018.
Models of energy loss from internal waves breaking in the ocean.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 836,
Issue. ,
p.
72.
Wang, David W.
and
Wijesekera, Hemantha W.
2018.
Observations of Breaking Waves and Energy Dissipation in Modulated Wave Groups.
Journal of Physical Oceanography,
Vol. 48,
Issue. 12,
p.
2937.
van den Bremer, T. S.
Whittaker, C.
Calvert, R.
Raby, A.
and
Taylor, P. H.
2019.
Experimental study of particle trajectories below deep-water surface gravity wave groups.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 879,
Issue. ,
p.
168.
Kalisch, Henrik
Ricchiuto, Mario
Bonneton, Philippe
Colin, Mathieu
and
Lubin, Pierre
2019.
Introduction to the Special Issue on Breaking Waves.
European Journal of Mechanics - B/Fluids,
Vol. 73,
Issue. ,
p.
1.
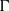 $\Gamma $, of the ensemble-average velocity field, due to the body force. By examining the relationship between a breaking wave and an impulsively forced fluid, we propose a functional form for the body force, allowing us to build upon the classical work on vortex ring phenomena to both quantify the circulation generated by a breaking wave and describe the vortex structure of the induced motion. Using scaling arguments, we show that
$\Gamma $, of the ensemble-average velocity field, due to the body force. By examining the relationship between a breaking wave and an impulsively forced fluid, we propose a functional form for the body force, allowing us to build upon the classical work on vortex ring phenomena to both quantify the circulation generated by a breaking wave and describe the vortex structure of the induced motion. Using scaling arguments, we show that 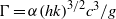 $\Gamma = \alpha {(hk)}^{3/ 2} {c}^{3} / g$, where (
$\Gamma = \alpha {(hk)}^{3/ 2} {c}^{3} / g$, where (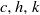 $c, h, k$) represent a characteristic speed, height and wavenumber of the breaking wave, respectively,
$c, h, k$) represent a characteristic speed, height and wavenumber of the breaking wave, respectively, 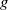 $g$ is the acceleration due to gravity and
$g$ is the acceleration due to gravity and  $\alpha $ is a constant. This then allows us to find a direct relationship between the circulation and the wave energy dissipation rate per unit crest length due to breaking,
$\alpha $ is a constant. This then allows us to find a direct relationship between the circulation and the wave energy dissipation rate per unit crest length due to breaking, 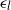 ${\epsilon }_{l} $. Finally, we compare our model and the available experimental data.
${\epsilon }_{l} $. Finally, we compare our model and the available experimental data.