Article contents
Vertically localised equilibrium solutions in large-eddy simulations of homogeneous shear flow
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 18 August 2017
Abstract
Unstable equilibrium solutions in a homogeneous shear flow with sinuous (streamwise-shift-reflection and spanwise-shift-rotation) symmetry are numerically found in large-eddy simulations (LES) with no kinetic viscosity. The small-scale properties are determined by the mixing length scale 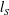 $l_{S}$ used to define eddy viscosity, and the large-scale motion is induced by the mean shear at the integral scale, which is limited by the spanwise box dimension
$l_{S}$ used to define eddy viscosity, and the large-scale motion is induced by the mean shear at the integral scale, which is limited by the spanwise box dimension 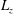 $L_{z}$. The fraction
$L_{z}$. The fraction 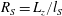 $R_{S}=L_{z}/l_{S}$, which plays the role of a Reynolds number, is used as a numerical continuation parameter. It is shown that equilibrium solutions appear by a saddle-node bifurcation as
$R_{S}=L_{z}/l_{S}$, which plays the role of a Reynolds number, is used as a numerical continuation parameter. It is shown that equilibrium solutions appear by a saddle-node bifurcation as 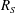 $R_{S}$ increases, and that the flow structures resemble those in plane Couette flow with the same sinuous symmetry. The vortical structures of both lower- and upper-branch solutions become spontaneously localised in the vertical direction. The lower-branch solution is an edge state at low
$R_{S}$ increases, and that the flow structures resemble those in plane Couette flow with the same sinuous symmetry. The vortical structures of both lower- and upper-branch solutions become spontaneously localised in the vertical direction. The lower-branch solution is an edge state at low 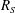 $R_{S}$, and takes the form of a thin critical layer as
$R_{S}$, and takes the form of a thin critical layer as 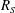 $R_{S}$ increases, as in the asymptotic theory of generic shear flow at high Reynolds numbers. On the other hand, the upper-branch solutions are characterised by a tall velocity streak with multiscale multiple vortical structures. At the higher end of
$R_{S}$ increases, as in the asymptotic theory of generic shear flow at high Reynolds numbers. On the other hand, the upper-branch solutions are characterised by a tall velocity streak with multiscale multiple vortical structures. At the higher end of 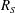 $R_{S}$, an incipient multiscale structure is found. The LES turbulence occasionally visits vertically localised states whose vortical structure resembles the present vertically localised LES equilibria.
$R_{S}$, an incipient multiscale structure is found. The LES turbulence occasionally visits vertically localised states whose vortical structure resembles the present vertically localised LES equilibria.
- Type
- Papers
- Information
- Copyright
- © 2017 Cambridge University Press
References
- 10
- Cited by



