Published online by Cambridge University Press: 24 July 2023
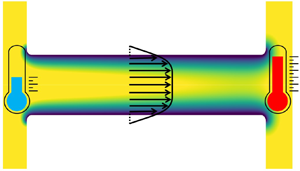
The thermo-osmotic flow (TOF) of an electrolyte solution in a slit channel with a Navier slip condition at the channel walls is studied. An analytical expression for the TOF velocity profile, based on the long-wavelength and Debye–Hückel approximations, is derived and compared to numerical solutions based on the finite-element method. The TOF between graphene surfaces whose charge is created via polarization through an applied electric field is considered as a special case. Using the relationship between the surface charge and the slip length obtained from molecular dynamics simulations, a giant flow amplification is uncovered. Specifically, for such flow in a channel with a width of 10 nm, compared to the flow between no-slip walls, a flow velocity enhancement by a factor of up to 250 is predicted.