Published online by Cambridge University Press: 04 July 2019
In this work, we theoretically investigate the swimming velocity of a Taylor swimming sheet immersed in a linearly density-stratified fluid. We use a regular perturbation expansion approach to estimate the swimming velocity up to second order in wave amplitude. We divide our analysis into two regimes of low (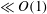 $\ll O(1)$) and finite Reynolds numbers. We use our solution to understand the effect of stratification on the swimming behaviour of organisms. We find that stratification significantly influences motility characteristics of the swimmer such as the swimming speed, hydrodynamic power expenditure, swimming efficiency and the induced mixing, quantified by mixing efficiency and diapycnal eddy diffusivity. We explore this dependence in detail for both low and finite Reynolds number and elucidate the fundamental insights obtained. We expect our work to shed some light on the importance of stratification in the locomotion of organisms living in density-stratified aquatic environments.
$\ll O(1)$) and finite Reynolds numbers. We use our solution to understand the effect of stratification on the swimming behaviour of organisms. We find that stratification significantly influences motility characteristics of the swimmer such as the swimming speed, hydrodynamic power expenditure, swimming efficiency and the induced mixing, quantified by mixing efficiency and diapycnal eddy diffusivity. We explore this dependence in detail for both low and finite Reynolds number and elucidate the fundamental insights obtained. We expect our work to shed some light on the importance of stratification in the locomotion of organisms living in density-stratified aquatic environments.