Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Pan, Zhenhai
Dash, Susmita
Weibel, Justin A.
and
Garimella, Suresh V.
2013.
Assessment of Water Droplet Evaporation Mechanisms on Hydrophobic and Superhydrophobic Substrates.
Langmuir,
Vol. 29,
Issue. 51,
p.
15831.
Weon, Byung Mook
and
Je, Jung Ho
2013.
Self-Pinning by Colloids Confined at a Contact Line.
Physical Review Letters,
Vol. 110,
Issue. 2,
Gelderblom, Hanneke
Stone, Howard A.
and
Snoeijer, Jacco H.
2013.
Stokes flow in a drop evaporating from a liquid subphase.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 25,
Issue. 10,
Verma, Gopal
and
Singh, Kamal P.
2014.
Time-resolved interference unveils nanoscale surface dynamics in evaporating sessile droplet.
Applied Physics Letters,
Vol. 104,
Issue. 24,
Ledesma-Aguilar, Rodrigo
Vella, Dominic
and
Yeomans, Julia M.
2014.
Lattice-Boltzmann simulations of droplet evaporation.
Soft Matter,
Vol. 10,
Issue. 41,
p.
8267.
Gentile, Francesco
Coluccio, Maria
Limongi, Tania
Perozziello, Gerardo
Candeloro, Patrizio
and
Di Fabrizio, Enzo
2014.
The Five Ws (and one H) of Super-Hydrophobic Surfaces in Medicine.
Micromachines,
Vol. 5,
Issue. 2,
p.
239.
Gentile, Francesco
Coluccio, Maria Laura
Zaccaria, Remo Proietti
Francardi, Marco
Cojoc, Gheorghe
Perozziello, Gerardo
Raimondo, Raffaella
Candeloro, Patrizio
and
Di Fabrizio, Enzo
2014.
Selective on site separation and detection of molecules in diluted solutions with super-hydrophobic clusters of plasmonic nanoparticles.
Nanoscale,
Vol. 6,
Issue. 14,
p.
8208.
Stauber, Jutta M.
Wilson, Stephen K.
Duffy, Brian R.
and
Sefiane, Khellil
2015.
On the lifetimes of evaporating droplets with related initial and receding contact angles.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 27,
Issue. 12,
Fontelos, Marco A.
Hong, Seok Hyun
and
Hwang, Hyung Ju
2015.
A Stable Self-Similar Singularity of Evaporating Drops: Ellipsoidal Collapse to a Point.
Archive for Rational Mechanics and Analysis,
Vol. 217,
Issue. 2,
p.
373.
Snoeijer, Jacco H.
and
van Wijngaarden, Leen
2015.
Interface deformations due to counter-rotating vortices: Viscous versus elastic media.
Physical Review E,
Vol. 91,
Issue. 3,
Soulié, Virginie
Karpitschka, Stefan
Lequien, Florence
Prené, Philippe
Zemb, Thomas
Moehwald, Helmuth
and
Riegler, Hans
2015.
The evaporation behavior of sessile droplets from aqueous saline solutions.
Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics,
Vol. 17,
Issue. 34,
p.
22296.
OLIVER, J. M.
WHITELEY, J. P.
SAXTON, M. A.
VELLA, D.
ZUBKOV, V. S.
and
KING, J. R.
2015.
On contact-line dynamics with mass transfer.
European Journal of Applied Mathematics,
Vol. 26,
Issue. 5,
p.
671.
Stauber, Jutta M.
Wilson, Stephen K.
Duffy, Brian R.
and
Sefiane, Khellil
2015.
Evaporation of Droplets on Strongly Hydrophobic Substrates.
Langmuir,
Vol. 31,
Issue. 12,
p.
3653.
Li, Bo
Iocozzia, James
and
Lin, Zhiqun
2015.
Polymer Surfaces in Motion.
p.
43.
Gentile, Francesco
Ferrara, Lorenzo
Villani, Marco
Bettelli, Manuele
Iannotta, Salvatore
Zappettini, Andrea
Cesarelli, Mario
Di Fabrizio, Enzo
and
Coppedè, Nicola
2016.
Geometrical Patterning of Super-Hydrophobic Biosensing Transistors Enables Space and Time Resolved Analysis of Biological Mixtures.
Scientific Reports,
Vol. 6,
Issue. 1,
Marin, Alvaro
Liepelt, Robert
Rossi, Massimiliano
and
Kähler, Christian J.
2016.
Surfactant-driven flow transitions in evaporating droplets.
Soft Matter,
Vol. 12,
Issue. 5,
p.
1593.
Al-Sharafi, Abdullah
Yilbas, Bekir S.
Ali, H.
and
Sahin, Ahmet Z.
2016.
Internal fluidity of a sessile droplet with the presence of particles on a hydrophobic surface.
Numerical Heat Transfer, Part A: Applications,
Vol. 70,
Issue. 10,
p.
1118.
Hong, Seok Hyun
Fontelos, Marco A.
and
Hwang, Hyung Ju
2016.
The contact line of an evaporating droplet over a solid wedge and the pinned–unpinned transition.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 791,
Issue. ,
p.
519.
Zheng, Zhenchen
Zhou, Leping
Du, Xiaoze
and
Yang, Yongping
2016.
Numerical investigation on conjugate heat transfer of evaporating thin film in a sessile droplet.
International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer,
Vol. 101,
Issue. ,
p.
10.
Saxton, M. A.
Whiteley, J. P.
Vella, D.
and
Oliver, J. M.
2016.
On thin evaporating drops: When is the -law valid?.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 792,
Issue. ,
p.
134.
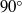 , the evaporative flux from the droplet tends to diverge in the vicinity of the contact line. Therefore, the description of the flow inside an evaporating drop has remained a challenge. Here, we focus on the asymptotic behaviour near the pinned contact line, by analytically solving the Stokes equations in a wedge geometry of arbitrary contact angle. The flow field is described by similarity solutions, with exponents that match the singular boundary condition due to evaporation. We demonstrate that there are three contributions to the flow in a wedge: the evaporative flux, the downward motion of the liquid–air interface and the eigenmode solution which fulfils the homogeneous boundary conditions. Below a critical contact angle of
, the evaporative flux from the droplet tends to diverge in the vicinity of the contact line. Therefore, the description of the flow inside an evaporating drop has remained a challenge. Here, we focus on the asymptotic behaviour near the pinned contact line, by analytically solving the Stokes equations in a wedge geometry of arbitrary contact angle. The flow field is described by similarity solutions, with exponents that match the singular boundary condition due to evaporation. We demonstrate that there are three contributions to the flow in a wedge: the evaporative flux, the downward motion of the liquid–air interface and the eigenmode solution which fulfils the homogeneous boundary conditions. Below a critical contact angle of 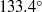 , the evaporative flux solution will dominate, while above this angle the eigenmode solution dominates. We demonstrate that for small contact angles, the velocity field is very accurately described by the lubrication approximation. For larger contact angles, the flow separates into regions where the flow is reversing towards the drop centre.
, the evaporative flux solution will dominate, while above this angle the eigenmode solution dominates. We demonstrate that for small contact angles, the velocity field is very accurately described by the lubrication approximation. For larger contact angles, the flow separates into regions where the flow is reversing towards the drop centre.

