Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Vimercati, Davide
Kluwick, Alfred
and
Guardone, Alberto
2018.
Oblique waves in steady supersonic flows of Bethe–Zel’dovich–Thompson fluids.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 855,
Issue. ,
p.
445.
Kluwick, A.
and
Cox, E. A.
2019.
Weak shock reflection in channel flows for dense gases.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 874,
Issue. ,
p.
131.
Kluwick, A.
and
Cox, E. A.
2019.
Steady transonic dense gas flow past two‐dimensional compression/expansion ramps revisited.
PAMM,
Vol. 19,
Issue. 1,
Vimercati, Davide
Kluwick, Alfred
and
Guardone, Alberto
2020.
Shock interactions in two-dimensional steady flows of Bethe–Zel’dovich–Thompson fluids.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 887,
Issue. ,
Rusak, Zvi
and
Virk, Akashdeep Singh
2021.
Transonic flows of single-phase supercritical fluids over thin airfoils.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 915,
Issue. ,
Tosto, Francesco
Lettieri, Claudio
Pini, Matteo
and
Colonna, Piero
2021.
Dense-vapor effects in compressible internal flows.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 33,
Issue. 8,
Volkov, K. N.
and
Emel’yanov, V. N.
2022.
Gas-Particle Flow around an Expansion Corner.
Russian Aeronautics,
Vol. 65,
Issue. 4,
p.
731.
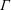 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}$) and its derivative with respect to the density at constant entropy (
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6E4}$) and its derivative with respect to the density at constant entropy (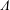 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$) in the small-disturbance limit. The resulting response to external forcing is surprisingly rich and studied in detail for the canonical problem of two-dimensional flow past compression/expansion ramps.
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$) in the small-disturbance limit. The resulting response to external forcing is surprisingly rich and studied in detail for the canonical problem of two-dimensional flow past compression/expansion ramps.