Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Tyvand, Peder A.
and
Nøland, Jonas Kristiansen
2021.
Transient nonlinear Rayleigh–Bénard convection with single-mode initiation.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 33,
Issue. 11,
Ding, Zijing
and
Wu, Jian
2021.
Coherent heat transport in two-dimensional penetrative Rayleigh–Bénard convection.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 920,
Issue. ,
Arslan, Ali
Fantuzzi, Giovanni
Craske, John
and
Wynn, Andrew
2021.
Bounds for internally heated convection with fixed boundary heat flux.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 922,
Issue. ,
Olson, Matthew L.
Goluskin, David
Schultz, William W.
and
Doering, Charles R.
2021.
Heat transport bounds for a truncated model of Rayleigh–Bénard convection via polynomial optimization.
Physica D: Nonlinear Phenomena,
Vol. 415,
Issue. ,
p.
132748.
Li, Xiao-Ming
He, Ji-Dong
Tian, Ye
Hao, Peng
and
Huang, Shi-Di
2021.
Effects of Prandtl number in quasi-two-dimensional Rayleigh–Bénard convection.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 915,
Issue. ,
O'Connor, Liam
Lecoanet, Daniel
and
Anders, Evan H.
2021.
Marginally stable thermal equilibria of Rayleigh-Bénard convection.
Physical Review Fluids,
Vol. 6,
Issue. 9,
Wen, Baole
Goluskin, David
and
Doering, Charles R.
2022.
Steady Rayleigh–Bénard convection between no-slip boundaries.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 933,
Issue. ,
Huang, Maojing
Wang, Yin
Bao, Yun
and
He, Xiaozhou
2022.
Heat transport and temperature boundary-layer profiles in closed turbulent Rayleigh–Bénard convection with slippery conducting surfaces.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 943,
Issue. ,
Lüdemann, K.
and
Tilgner, A.
2022.
Transition to three-dimensional flow in thermal convection with spanwise rotation.
Physical Review Fluids,
Vol. 7,
Issue. 6,
Drivas, Theodore D.
Nguyen, Huy Q.
and
Nobili, Camilla
2022.
Bounds on heat flux for Rayleigh–Bénard convection between Navier-slip fixed-temperature boundaries.
Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences,
Vol. 380,
Issue. 2225,
Bouillaut, Vincent
Flesselles, Benoît
Miquel, Benjamin
Aumaître, Sébastien
and
Gallet, Basile
2022.
Velocity-informed upper bounds on the convective heat transport induced by internal heat sources and sinks.
Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences,
Vol. 380,
Issue. 2225,
Motoki, Shingo
Kawahara, Genta
and
Shimizu, Masaki
2022.
Steady thermal convection representing the ultimate scaling.
Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences,
Vol. 380,
Issue. 2225,
Winchester, Philip
Howell, Peter D.
and
Dallas, Vassilios
2022.
The onset of zonal modes in two-dimensional Rayleigh–Bénard convection.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 939,
Issue. ,
Nobili, Camilla
2022.
The role of boundary conditions in scaling laws for turbulent heat transport.
Mathematics in Engineering,
Vol. 5,
Issue. 1,
p.
1.
Huang, Maojing
and
He, Xiaozhou
2022.
Heat transport in horizontally periodic and confined Rayleigh-Bénard convection with no-slip and free-slip plates.
Theoretical and Applied Mechanics Letters,
Vol. 12,
Issue. 2,
p.
100330.
Huang, Maojing
and
He, Xiaozhou
2022.
Effect of slip length on flow dynamics and heat transport in two-dimensional Rayleigh–Bénard convection.
Journal of Turbulence,
Vol. 23,
Issue. 9-10,
p.
492.
Reiter, Philipp
Zhang, Xuan
and
Shishkina, Olga
2022.
Flow states and heat transport in Rayleigh–Bénard convection with different sidewall boundary conditions.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 936,
Issue. ,
Wen, Baole
Ding, Zijing
Chini, Gregory P.
and
Kerswell, Rich R.
2022.
Heat transport in Rayleigh–Bénard convection with linear marginality.
Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences,
Vol. 380,
Issue. 2225,
Kumar, Anuj
Arslan, Ali
Fantuzzi, Giovanni
Craske, John
and
Wynn, Andrew
2022.
Analytical bounds on the heat transport in internally heated convection.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 938,
Issue. ,
Abbate, Jewel A.
and
Aurnou, Jonathan M.
2023.
Rotating convective turbulence in moderate to high Prandtl number fluids.
Geophysical & Astrophysical Fluid Dynamics,
Vol. 117,
Issue. 6,
p.
397.
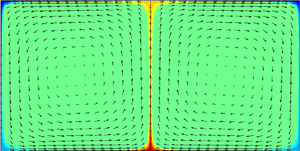
 ${\rm \pi} /5\leqslant \varGamma \leqslant 4{\rm \pi}$, where
${\rm \pi} /5\leqslant \varGamma \leqslant 4{\rm \pi}$, where  $\varGamma$ is the width-to-height ratio for a pair of counter-rotating rolls, over eight orders of magnitude in the Rayleigh number,
$\varGamma$ is the width-to-height ratio for a pair of counter-rotating rolls, over eight orders of magnitude in the Rayleigh number,  $10^3\leqslant Ra\leqslant 10^{11}$, and four orders of magnitude in the Prandtl number,
$10^3\leqslant Ra\leqslant 10^{11}$, and four orders of magnitude in the Prandtl number,  $10^{-2}\leqslant Pr\leqslant 10^2$. At large
$10^{-2}\leqslant Pr\leqslant 10^2$. At large  $Ra$ where steady rolls are dynamically unstable, the computed rolls display
$Ra$ where steady rolls are dynamically unstable, the computed rolls display  $Ra \rightarrow \infty$ asymptotic scaling. In this regime, the Nusselt number
$Ra \rightarrow \infty$ asymptotic scaling. In this regime, the Nusselt number  $Nu$ that measures heat transport scales as
$Nu$ that measures heat transport scales as  $Ra^{1/3}$ uniformly in
$Ra^{1/3}$ uniformly in  $Pr$. The prefactor of this scaling depends on
$Pr$. The prefactor of this scaling depends on  $\varGamma$ and is largest at
$\varGamma$ and is largest at  $\varGamma \approx 1.9$. The Reynolds number
$\varGamma \approx 1.9$. The Reynolds number  $Re$ for large-
$Re$ for large- $Ra$ rolls scales as
$Ra$ rolls scales as  $Pr^{-1} Ra^{2/3}$ with a prefactor that is largest at
$Pr^{-1} Ra^{2/3}$ with a prefactor that is largest at  $\varGamma \approx 4.5$. All of these large-
$\varGamma \approx 4.5$. All of these large- $Ra$ features agree quantitatively with the semi-analytical asymptotic solutions constructed by Chini & Cox (Phys. Fluids, vol. 21, 2009, 083603). Convergence of
$Ra$ features agree quantitatively with the semi-analytical asymptotic solutions constructed by Chini & Cox (Phys. Fluids, vol. 21, 2009, 083603). Convergence of  $Nu$ and
$Nu$ and  $Re$ to their asymptotic scalings occurs more slowly when
$Re$ to their asymptotic scalings occurs more slowly when  $Pr$ is larger and when
$Pr$ is larger and when  $\varGamma$ is smaller.
$\varGamma$ is smaller.