Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Meldi, M.
and
Sagaut, P.
2013.
Further insights into self-similarity and self-preservation in freely decaying isotropic turbulence.
Journal of Turbulence,
Vol. 14,
Issue. 8,
p.
24.
Meldi, Marcello
Lejemble, Hugo
and
Sagaut, Pierre
2014.
On the emergence of non-classical decay regimes in multiscale/fractal generated isotropic turbulence.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 756,
Issue. ,
p.
816.
Meldi, M.
and
Sagaut, P.
2014.
An adaptive numerical method for solving EDQNM equations for the analysis of long-time decay of isotropic turbulence.
Journal of Computational Physics,
Vol. 262,
Issue. ,
p.
72.
Zhao, Sipei
Cheng, Eva
Qiu, Xiaojun
Burnett, Ian
and
Liu, Jacob Chia-chun
2016.
Pressure spectra in turbulent flows in the inertial and the dissipation ranges.
The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America,
Vol. 140,
Issue. 6,
p.
4178.
Meldi, M.
2016.
The signature of initial production mechanisms in isotropic turbulence decay.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 28,
Issue. 3,
Briard, Antoine
Iyer, Manasa
and
Gomez, Thomas
2017.
Anisotropic spectral modeling for unstably stratified homogeneous turbulence.
Physical Review Fluids,
Vol. 2,
Issue. 4,
Zhao, Sipei
Cheng, Eva
Qiu, Xiaojun
Burnett, Ian
and
Liu, Jacob Chia-chun
2017.
Wind noise spectra in small Reynolds number turbulent flows.
The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America,
Vol. 142,
Issue. 5,
p.
3227.
Tang, S. L.
Antonia, R. A.
Djenidi, L.
Danaila, L.
and
Zhou, Y.
2017.
Finite Reynolds number effect on the scaling range behaviour of turbulent longitudinal velocity structure functions.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 820,
Issue. ,
p.
341.
Antonia, R. A.
Djenidi, L.
Danaila, L.
and
Tang, S. L.
2017.
Small scale turbulence and the finite Reynolds number effect.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 29,
Issue. 2,
Meldi, M.
and
Sagaut, P.
2017.
Turbulence in a box: quantification of large-scale resolution effects in isotropic turbulence free decay.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 818,
Issue. ,
p.
697.
Slama, Myriam
Leblond, Cédric
and
Sagaut, Pierre
2018.
A Kriging-based elliptic extended anisotropic model for the turbulent boundary layer wall pressure spectrum.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 840,
Issue. ,
p.
25.
Sagaut, Pierre
and
Cambon, Claude
2018.
Homogeneous Turbulence Dynamics.
p.
99.
Hoque, Mohammad Mainul
Mitra, Subhasish
Evans, Geoffrey M.
Pareek, Vishnu
and
Joshi, Jyeshtharaj B.
2018.
Effect of bubble on the pressure spectra of oscillating grid turbulent flow at low Taylor-Reynolds number.
Chemical Engineering Science,
Vol. 190,
Issue. ,
p.
28.
Meldi, Marcello
and
Sagaut, Pierre
2018.
Investigation of anomalous very fast decay regimes in homogeneous isotropic turbulence.
Journal of Turbulence,
Vol. 19,
Issue. 5,
p.
390.
Meldi, M.
Djenidi, L.
and
Antonia, R.
2018.
Reynolds number effect on the velocity derivative flatness factor.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 856,
Issue. ,
p.
426.
Antonia, R. A.
Tang, S. L.
Danaila, L.
Djenidi, L.
and
Zhou, Y.
2019.
Fluid-Structure-Sound Interactions and Control.
p.
3.
Zheng, Qinmin
Wang, Jianchun
Mahbub Alam, Md.
Noack, Bernd R.
Li, Hui
and
Chen, Shiyi
2021.
Transfer of internal energy fluctuation in compressible isotropic turbulence with vibrational non-equilibrium.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 919,
Issue. ,
Hirabayashi, Riku
Suzuki, Hiroki
and
Mochizuki, Shinsuke
2023.
LES analysis clarifying the response of static pressure fluctuation characteristics in isotropic/anisotropic steady turbulence field to reducing isotropic small-scale spatial resolution.
Journal of Physics: Conference Series,
Vol. 2585,
Issue. 1,
p.
012006.
Tang, Shunlin
Danaila, Luminita
and
Antonia, Robert Anthony
2024.
Finite Reynolds Number Effect on Small-Scale Statistics in Decaying Grid Turbulence.
Atmosphere,
Vol. 15,
Issue. 5,
p.
540.
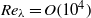 $R{e}_{\lambda } = O(1{0}^{4} )$ must be considered to observe a one-decade inertial range in the pressure spectrum with Kolmogorov
$R{e}_{\lambda } = O(1{0}^{4} )$ must be considered to observe a one-decade inertial range in the pressure spectrum with Kolmogorov  $- 7/ 3$ scaling. This threshold value is larger than almost all existing direct numerical simulation (DNS) and experimental data, justifying the discussion about other possible scaling laws. The
$- 7/ 3$ scaling. This threshold value is larger than almost all existing direct numerical simulation (DNS) and experimental data, justifying the discussion about other possible scaling laws. The  $- 5/ 3$ slope reported in some DNS data is also recovered by the EDQNM model, but it is observed to be a low-Reynolds-number effect. Another important result is that FRN effects yield a departure from asymptotic theoretical behaviours which appear similar to some effects attributed to intermittency by most authors. This is exemplified by the ratio between pressure-based and velocity-based Taylor microscales. Therefore, high-Reynolds-number DNS or experiments such that
$- 5/ 3$ slope reported in some DNS data is also recovered by the EDQNM model, but it is observed to be a low-Reynolds-number effect. Another important result is that FRN effects yield a departure from asymptotic theoretical behaviours which appear similar to some effects attributed to intermittency by most authors. This is exemplified by the ratio between pressure-based and velocity-based Taylor microscales. Therefore, high-Reynolds-number DNS or experiments such that 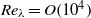 $R{e}_{\lambda } = O(1{0}^{4} )$ would be required in order to remove FRN effects and to analyse pure intermittency effects.
$R{e}_{\lambda } = O(1{0}^{4} )$ would be required in order to remove FRN effects and to analyse pure intermittency effects.