Published online by Cambridge University Press: 01 December 2015
Well-resolved measurements of the small-scale dissipation statistics within turbulent channel flow are reported for a range of Reynolds numbers from 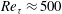 $Re_{{\it\tau}}\approx 500$ to 4000. In this flow, the local large-scale Reynolds number based on the longitudinal integral length scale is found to poorly describe the Reynolds number dependence of the small-scale statistics. When a length scale based on Townsend’s attached-eddy hypothesis is used to define the local large-scale Reynolds number, the Reynolds number scaling behaviour was found to be more consistent with that observed in homogeneous, isotropic turbulence. The Reynolds number scaling of the dissipation moments up to the sixth moment was examined and the results were found to be in good agreement with predicted scaling behaviour (Schumacher et al., Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA, vol. 111, 2014, pp. 10961–10965). The probability density functions of the local dissipation scales (Yakhot, Physica D, vol. 215 (2), 2006, pp. 166–174) were also determined and, when the revised local large-scale Reynolds number is used for normalization, provide support for the existence of a universal distribution which scales differently for inner and outer regions.
$Re_{{\it\tau}}\approx 500$ to 4000. In this flow, the local large-scale Reynolds number based on the longitudinal integral length scale is found to poorly describe the Reynolds number dependence of the small-scale statistics. When a length scale based on Townsend’s attached-eddy hypothesis is used to define the local large-scale Reynolds number, the Reynolds number scaling behaviour was found to be more consistent with that observed in homogeneous, isotropic turbulence. The Reynolds number scaling of the dissipation moments up to the sixth moment was examined and the results were found to be in good agreement with predicted scaling behaviour (Schumacher et al., Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA, vol. 111, 2014, pp. 10961–10965). The probability density functions of the local dissipation scales (Yakhot, Physica D, vol. 215 (2), 2006, pp. 166–174) were also determined and, when the revised local large-scale Reynolds number is used for normalization, provide support for the existence of a universal distribution which scales differently for inner and outer regions.