Article contents
Moisture transfer by turbulent natural convection
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 15 July 2019
Abstract
We present an experimental and numerical study of natural convection with moist air as convecting fluid. By simplifying the system as two-component convection, an experimental method is proposed for indirectly measuring the moisture transfer rates in buoyancy-driven flows. We verify the results using direct numerical simulations. It is found that the non-dimensionalized transfer rates for both sensible heat (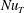 $Nu_{T}$) and water vapour (
$Nu_{T}$) and water vapour (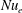 $Nu_{e}$) are essentially determined by a generalized Grashof number
$Nu_{e}$) are essentially determined by a generalized Grashof number 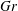 $Gr$ (the ratio of combined buoyancy generated by the imposed temperature and vapour pressure gradients to viscous force), and are only weakly dependent on the buoyancy ratio
$Gr$ (the ratio of combined buoyancy generated by the imposed temperature and vapour pressure gradients to viscous force), and are only weakly dependent on the buoyancy ratio 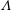 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$ (the ratio of buoyancy induced by temperature variation to that due to vapour pressure variation). Moreover, we show that the full set of control parameters
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC}$ (the ratio of buoyancy induced by temperature variation to that due to vapour pressure variation). Moreover, we show that the full set of control parameters 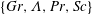 $\{Gr,\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC},Pr,Sc\}$ is more suitable than other choices for characterizing the two-component system under investigation. As a special case, the Schmidt number dependence for passive scalar transport rates in buoyancy-driven flows is also deduced.
$\{Gr,\unicode[STIX]{x1D6EC},Pr,Sc\}$ is more suitable than other choices for characterizing the two-component system under investigation. As a special case, the Schmidt number dependence for passive scalar transport rates in buoyancy-driven flows is also deduced.
JFM classification
- Type
- JFM Papers
- Information
- Copyright
- © 2019 Cambridge University Press
References
- 7
- Cited by



