Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Shishkina, Olga
and
Wagner, Claus
2012.
A numerical study of turbulent mixed convection in an enclosure with heated rectangular elements.
Journal of Turbulence,
Vol. 13,
Issue. ,
p.
N22.
Chillà, F.
and
Schumacher, J.
2012.
New perspectives in turbulent Rayleigh-Bénard convection.
The European Physical Journal E,
Vol. 35,
Issue. 7,
Dey, Ranabir
DasGupta, Sunando
and
Chakraborty, Suman
2012.
Thermally activated control of microfluidic friction.
Applied Physics Letters,
Vol. 101,
Issue. 13,
Shishkina, Olga
Horn, Susanne
and
Wagner, Sebastian
2013.
Falkner–Skan boundary layer approximation in Rayleigh–Bénard convection.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 730,
Issue. ,
p.
442.
Hossain, M. Z.
and
Floryan, J. M.
2014.
Natural convection in a fluid layer periodically heated from above.
Physical Review E,
Vol. 90,
Issue. 2,
Shishkina, Olga
Wagner, Sebastian
and
Horn, Susanne
2014.
Influence of the angle between the wind and the isothermal surfaces on the boundary layer structures in turbulent thermal convection.
Physical Review E,
Vol. 89,
Issue. 3,
Shishkina, Olga
and
Wagner, Claus
2014.
New Results in Numerical and Experimental Fluid Mechanics IX.
Vol. 124,
Issue. ,
p.
303.
Ripesi, P.
Biferale, L.
Sbragaglia, M.
and
Wirth, A.
2014.
Natural convection with mixed insulating and conducting boundary conditions: low- and high-Rayleigh-number regimes.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 742,
Issue. ,
p.
636.
Salort, J.
Liot, O.
Rusaouen, E.
Seychelles, F.
Tisserand, J.-C.
Creyssels, M.
Castaing, B.
and
Chillà, F.
2014.
Thermal boundary layer near roughnesses in turbulent Rayleigh-Bénard convection: Flow structure and multistability.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 26,
Issue. 1,
Wagner, Sebastian
and
Shishkina, Olga
2015.
Heat flux enhancement by regular surface roughness in turbulent thermal convection.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 763,
Issue. ,
p.
109.
Wagner, S.
and
Shishkina, O.
2015.
Direct and Large-Eddy Simulation IX.
Vol. 20,
Issue. ,
p.
337.
Toppaladoddi, Srikanth
Succi, Sauro
and
Wettlaufer, John S.
2015.
Tailoring boundary geometry to optimize heat transport in turbulent convection.
EPL (Europhysics Letters),
Vol. 111,
Issue. 4,
p.
44005.
Toppaladoddi, Srikanth
Succi, Sauro
and
Wettlaufer, John S.
2015.
Turbulent Transport Processes at Rough Surfaces with Geophysical Applications.
Procedia IUTAM,
Vol. 15,
Issue. ,
p.
34.
Yousaf, M.
and
Usman, S.
2015.
Natural convection heat transfer in a square cavity with sinusoidal roughness elements.
International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer,
Vol. 90,
Issue. ,
p.
180.
Shishkina, Olga
2016.
Momentum and heat transport scalings in laminar vertical convection.
Physical Review E,
Vol. 93,
Issue. 5,
Guha, Abhijit
and
Sengupta, Sayantan
2016.
Effects of finiteness on the thermo-fluid-dynamics of natural convection above horizontal plates.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 28,
Issue. 6,
Liot, O.
Salort, J.
Kaiser, R.
du Puits, R.
and
Chillà, F.
2016.
Boundary layer structure in a rough Rayleigh–Bénard cell filled with air.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 786,
Issue. ,
p.
275.
Sheremet, M.A.
Cimpean, D.S.
and
Pop, I.
2017.
Free convection in a partially heated wavy porous cavity filled with a nanofluid under the effects of Brownian diffusion and thermophoresis.
Applied Thermal Engineering,
Vol. 113,
Issue. ,
p.
413.
Xie, Yi-Chao
and
Xia, Ke-Qing
2017.
Turbulent thermal convection over rough plates with varying roughness geometries.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 825,
Issue. ,
p.
573.
Liot, Olivier
Ehlinger, Quentin
Rusaouën, Éléonore
Coudarchet, Thibaut
Salort, Julien
and
Chillà, Francesca
2017.
Velocity fluctuations and boundary layer structure in a rough Rayleigh-Bénard cell filled with water.
Physical Review Fluids,
Vol. 2,
Issue. 4,
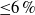 for all investigated cases.
for all investigated cases.

