Article contents
Mechanical energy budget and mixing efficiency for a radiatively heated ice-covered waterbody
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 03 August 2018
Abstract
Ice-covered waterbodies are far from being quiescent systems. In this paper, we investigate ice-covered freshwater basins heated by solar radiation that penetrates across waters with temperatures below or near the temperature of maximum density. In this scenario, solar radiation sets a radiative buoyancy flux, 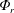 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6F7}_{r}$, that forces increments of temperature/density in the upper fluid volume, which can become gravitationally unstable and drive convection. The goal of this study is twofold. We first focus on formulating the mechanical energy budget, putting emphasis on the conversion of
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6F7}_{r}$, that forces increments of temperature/density in the upper fluid volume, which can become gravitationally unstable and drive convection. The goal of this study is twofold. We first focus on formulating the mechanical energy budget, putting emphasis on the conversion of 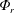 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6F7}_{r}$ to available potential energy,
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6F7}_{r}$ to available potential energy, 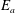 $E_{a}$. We find that
$E_{a}$. We find that 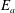 $E_{a}$ results from a competition among
$E_{a}$ results from a competition among 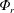 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6F7}_{r}$ and the irreversible mixing controlled by the diapycnal and the laminar mixing rates, respectively. Secondly, and based on the above result, we introduce an integral formulation of the mixing efficiency to quantify the rate of mixing over the relevant time scale
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6F7}_{r}$ and the irreversible mixing controlled by the diapycnal and the laminar mixing rates, respectively. Secondly, and based on the above result, we introduce an integral formulation of the mixing efficiency to quantify the rate of mixing over the relevant time scale  $\unicode[STIX]{x1D70F}$,
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D70F}$, 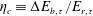 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D702}_{c}\equiv \unicode[STIX]{x0394}E_{b,\unicode[STIX]{x1D70F}}/E_{r,\unicode[STIX]{x1D70F}}$, where
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D702}_{c}\equiv \unicode[STIX]{x0394}E_{b,\unicode[STIX]{x1D70F}}/E_{r,\unicode[STIX]{x1D70F}}$, where 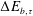 $\unicode[STIX]{x0394}E_{b,\unicode[STIX]{x1D70F}}$ and
$\unicode[STIX]{x0394}E_{b,\unicode[STIX]{x1D70F}}$ and 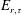 $E_{r,\unicode[STIX]{x1D70F}}$ are the change of background potential energy and the time-integrated
$E_{r,\unicode[STIX]{x1D70F}}$ are the change of background potential energy and the time-integrated 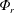 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6F7}_{r}$ over
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6F7}_{r}$ over  $\unicode[STIX]{x1D70F}$. The above definition is applied to estimate
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D70F}$. The above definition is applied to estimate 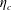 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D702}_{c}$ for the first time, finding an approximate value of
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D702}_{c}$ for the first time, finding an approximate value of 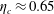 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D702}_{c}\approx 0.65$. This result suggests that radiatively heated ice-covered waterbodies might be subject to high mixing rates. Overall, the present work provides a framework to examine energetics and mixing in ice-covered waters.
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D702}_{c}\approx 0.65$. This result suggests that radiatively heated ice-covered waterbodies might be subject to high mixing rates. Overall, the present work provides a framework to examine energetics and mixing in ice-covered waters.
- Type
- JFM Rapids
- Information
- Copyright
- © 2018 Cambridge University Press
References
- 30
- Cited by


