Published online by Cambridge University Press: 19 August 2019
The plane wall jet (PWJ) is a wall-bounded flow in which a wall shear layer develops in the presence of extremely energetic flow structures of the outer free-shear layer. The structure of a PWJ, developing in still air, was studied with the focus on the large scales in the flow. Wall-normal hot-wire anemometry (HWA) measurements along with double-frame particle image velocimetry (PIV) measurements (wall-normal–streamwise plane) were carried out at streamwise distances up to 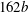 $162b$, where
$162b$, where 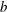 $b$ is the slot width of the PWJ exit. The nominal PWJ Reynolds number based on exit parameters was
$b$ is the slot width of the PWJ exit. The nominal PWJ Reynolds number based on exit parameters was 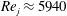 $Re_{j}\approx 5940$. Comparisons with a zero-pressure-gradient boundary layer (ZPGBL) at nominally matched friction Reynolds number
$Re_{j}\approx 5940$. Comparisons with a zero-pressure-gradient boundary layer (ZPGBL) at nominally matched friction Reynolds number 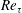 $Re_{\unicode[STIX]{x1D70F}}$ were also carried out as appropriate, to highlight key features of the PWJ structure. Consistent with previous work, the PWJ showed a dependence of the peak turbulent stresses on the jet exit Reynolds number. The turbulent production showed a peak corresponding to the near-wall cycle similar to the peak seen in the ZPGBL. However, another turbulent production peak was observed in the outer free-shear layer that was an order of magnitude larger than the inner one. Along with the change in sign of the viscous and Reynolds shear stresses, the PWJ was shown to have a region of very low turbulent production between these two peaks. The dissipation rate increased over the PWJ layer with a peak also in the outer region. Visualizations of the flow and two-point correlations reveal that the most energetic large-scale structures within a PWJ are vortical motions in the wall-normal–streamwise plane similar to those structures seen in free-shear layers. These structures are referred to as J (for jet) type structures. In addition two-point correlations reveal the existence of large-scale structures in the wall region which have a signature similar to those structures seen in canonical boundary layers. These structures are referred to as W (for wall) type structures. Instantaneous PIV realizations and flow visualizations reveal that these W type large-scale features are consistent with the paradigm of hairpin vortex packets in the wall region. The J type structures were seen to intrude well into the wall region while the W type structures were also seen to extend into the outer shear layer. Further, these large-scale structures were shown to modulate the amplitude of the finer scales of the flow.
$Re_{\unicode[STIX]{x1D70F}}$ were also carried out as appropriate, to highlight key features of the PWJ structure. Consistent with previous work, the PWJ showed a dependence of the peak turbulent stresses on the jet exit Reynolds number. The turbulent production showed a peak corresponding to the near-wall cycle similar to the peak seen in the ZPGBL. However, another turbulent production peak was observed in the outer free-shear layer that was an order of magnitude larger than the inner one. Along with the change in sign of the viscous and Reynolds shear stresses, the PWJ was shown to have a region of very low turbulent production between these two peaks. The dissipation rate increased over the PWJ layer with a peak also in the outer region. Visualizations of the flow and two-point correlations reveal that the most energetic large-scale structures within a PWJ are vortical motions in the wall-normal–streamwise plane similar to those structures seen in free-shear layers. These structures are referred to as J (for jet) type structures. In addition two-point correlations reveal the existence of large-scale structures in the wall region which have a signature similar to those structures seen in canonical boundary layers. These structures are referred to as W (for wall) type structures. Instantaneous PIV realizations and flow visualizations reveal that these W type large-scale features are consistent with the paradigm of hairpin vortex packets in the wall region. The J type structures were seen to intrude well into the wall region while the W type structures were also seen to extend into the outer shear layer. Further, these large-scale structures were shown to modulate the amplitude of the finer scales of the flow.
Large-scale temporal evolution of the flow. Here, nominal values of the relevant scales at $x/b=137$ have been used to carry out non-dimensionalization. Also shown are the nominal locations of the outer length scale $\delta$ and the location of the maximum velocity $z_m$ at $x/b=137$.
Identical to Movie 1 but with two zoomed-in views of the near-wall region, highlighting specific instantaneous flow structures. Here, nominal values of the relevant scales at $x/b=137$ have been used to carry out non-dimensionalization. Also shown are the nominal locations of the outer length scale $\delta$ and the location of the maximum velocity $z_m$ at $x/b=137$.