Published online by Cambridge University Press: 01 October 2019
Submesoscale currents, small-scale turbulence and surface gravity waves co-exist in the upper ocean and interact in complex ways. To expose the couplings, the frontogenetic life cycle of an idealized cold dense submesoscale filament interacting with upper ocean Langmuir turbulence is investigated in large-eddy simulations (LESs) based on the incompressible wave-averaged equations. The simulations utilize large domains and fine meshes with 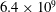 $6.4\times 10^{9}$ grid points. Case studies are made with surface winds or surface cooling with waves oriented in across-filament (perpendicular) or down-filament (parallel) directions relative to the two-dimensional filament axis. The currents
$6.4\times 10^{9}$ grid points. Case studies are made with surface winds or surface cooling with waves oriented in across-filament (perpendicular) or down-filament (parallel) directions relative to the two-dimensional filament axis. The currents  $u$,
$u$,  $v$ and
$v$ and 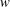 $w$ are aligned with the across-filament, down-filament and vertical directions, respectively. Frontogenesis is induced by across-filament Lagrangian secondary circulations in the boundary layer, and it is shown to be strongly impacted by surface waves, in particular the propagation direction relative to the filament axis. In a horizontally heterogeneous boundary layer, surface waves induce both mean and fluctuating Stokes-drift vortex forces that modify a linear, hydrostatic turbulent thermal wind (TTW) approximation for momentum. Down-filament winds and waves are found to be especially impactful, they significantly reduce the peak level of frontogenesis by fragmenting the filament into primary and secondary down-welling sites in a broad frontal zone over a width
$w$ are aligned with the across-filament, down-filament and vertical directions, respectively. Frontogenesis is induced by across-filament Lagrangian secondary circulations in the boundary layer, and it is shown to be strongly impacted by surface waves, in particular the propagation direction relative to the filament axis. In a horizontally heterogeneous boundary layer, surface waves induce both mean and fluctuating Stokes-drift vortex forces that modify a linear, hydrostatic turbulent thermal wind (TTW) approximation for momentum. Down-filament winds and waves are found to be especially impactful, they significantly reduce the peak level of frontogenesis by fragmenting the filament into primary and secondary down-welling sites in a broad frontal zone over a width 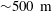 ${\sim}500~\text{m}$. At peak frontogenesis, opposing down-filament jets
${\sim}500~\text{m}$. At peak frontogenesis, opposing down-filament jets 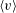 $\langle v\rangle$ overlie each other resulting in a vigorous vertical shear layer
$\langle v\rangle$ overlie each other resulting in a vigorous vertical shear layer 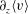 $\unicode[STIX]{x2202}_{z}\langle v\rangle$ with large vertical momentum flux
$\unicode[STIX]{x2202}_{z}\langle v\rangle$ with large vertical momentum flux 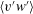 $\langle v^{\prime }w^{\prime }\rangle$. Filament arrest is induced by a lateral shear instability that generates horizontal momentum flux
$\langle v^{\prime }w^{\prime }\rangle$. Filament arrest is induced by a lateral shear instability that generates horizontal momentum flux 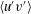 $\langle u^{\prime }v^{\prime }\rangle$ at low wavenumbers. The turbulent vertical velocity patterns, indicative of coherent Langmuir cells, change markedly across the horizontal domain with both across-filament and down-filament winds under the action of submesoscale currents.
$\langle u^{\prime }v^{\prime }\rangle$ at low wavenumbers. The turbulent vertical velocity patterns, indicative of coherent Langmuir cells, change markedly across the horizontal domain with both across-filament and down-filament winds under the action of submesoscale currents.