Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Benard, Nicolas
Laizet, Sylvain
and
Moreau, Eric
2017.
PIV-based dynamic model of EHD volume force produced by a surface dielectric barrier discharge.
Bian, Dong-Liang
Wu, Yun
Jia, Min
and
Long, Chang-Bai
2017.
PI/Al2O3 nanocomposite based long lifetime surface dielectric barrier discharge plasma actuator.
Sensors and Actuators A: Physical,
Vol. 267,
Issue. ,
p.
90.
Simon, Bernhard
Markus, Daniel
Tropea, Cameron
and
Grundmann, Sven
2018.
Cancellation of Tollmien–Schlichting Waves in Direct Vicinity of a Plasma Actuator.
AIAA Journal,
Vol. 56,
Issue. 5,
p.
1760.
Masati, A.
and
Sedwick, R. J.
2018.
Correcting for particle size effects on plasma actuator particle image velocimetry measurements.
Journal of Applied Physics,
Vol. 123,
Issue. 1,
Tang, Yong
Yao, Qiang
Cui, Wei
Pu, Yikang
and
Li, Shuiqing
2018.
Flow fluctuation induced by coaxial plasma device at atmospheric pressure.
Applied Physics Letters,
Vol. 113,
Issue. 22,
Dong‐liang, Bian
Yun, Wu
and
Min, Jia
2018.
Characterization of surface dielectric barrier discharge (SDBD) based on PI/Al2O3 nanocomposite.
Plasma Processes and Polymers,
Vol. 15,
Issue. 7,
Hehner, Marc T.
Gatti, Davide
and
Kriegseis, Jochen
2019.
Stokes-layer formation under absence of moving parts—A novel oscillatory plasma actuator design for turbulent drag reduction.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 31,
Issue. 5,
Zhang, Xin
Cui, Yongdong
Tay, Jonathan Chien Ming
and
Khoo, Boo Cheong
2020.
Unsteady Flow Structures Induced by a Single Microsecond Pulsed DBD Plasma Actuator in Quiescent Air.
Zhang, Xin
Cui, Y. D.
Tay, Jonathan Chien Ming
and
Khoo, B. C.
2020.
Unsteady Flow Structures Induced by Single Microsecond-Pulsed Plasma Actuator.
AIAA Journal,
Vol. 58,
Issue. 7,
p.
2820.
Bocharnikov, V. M.
Volodin, V. V.
Golub, V. V.
Trifanov, I. V.
and
Serebryakov, D. G.
2020.
Resonance Properties of a Low-Pressure Dielectric Barrier Discharge.
Technical Physics,
Vol. 65,
Issue. 12,
p.
1969.
Nonomura, Taku
Ozawa, Yuta
Ibuki, Takuma
Nankai, Koki
Komuro, Atsushi
Nishida, Hiroyuki
Marios, Kotsonis
Kubo, Noritsugu
and
Kawabata, Hirokazu
2020.
Single-Pixel Particle Image Velocimetry for Characterization of Dielectric Barrier Discharge Plasma Actuators.
AIAA Journal,
Vol. 58,
Issue. 11,
p.
4952.
Zhang, Xin
Cui, Y D
Tay, Chien-Ming Jonathan
and
Khoo, B C
2020.
Ultrasound generated by alternating current dielectric barrier discharge plasma in quiescent air.
Plasma Sources Science and Technology,
Vol. 29,
Issue. 1,
p.
015017.
Liao, Yu.
Mursenkova, I. V.
Ivanov, I. E.
Znamenskaya, I. A.
and
Sysoev, N. N.
2020.
Shock waves generated by a pulsed surface sliding discharge in a supersonic airflow past a wedge.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 32,
Issue. 10,
Jiang, Hui
Li, Wenhui
Xu, Yaozong
Liu, Haibo
Tan, Jianwen
and
Shao, Tao
2021.
Influence of segmented grounding electrodes on electrical characteristics in annular surface dielectric barrier discharge.
Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics,
Vol. 54,
Issue. 26,
p.
265203.
Kourtzanidis, K
Dufour, G
and
Rogier, F
2021.
The electrohydrodynamic force distribution in surface AC dielectric barrier discharge actuators: do streamers dictate the ionic wind profiles?.
Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics,
Vol. 54,
Issue. 26,
p.
26LT01.
Hehner, Marc T
Gatti, Davide
Kotsonis, Marios
and
Kriegseis, Jochen
2022.
Effects of actuation mode on plasma-induced spanwise flow oscillations.
Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics,
Vol. 55,
Issue. 20,
p.
205203.
Zhang, Xin
and
Qu, Feng
2022.
Formation Mechanism of Wall Jet Generated by Plasma Actuators in Quiescent Air.
AIAA Journal,
Vol. 60,
Issue. 8,
p.
4714.
Zhang, Xin
and
Wang, Yong
2022.
Spatial–temporal evolution of the pressure field generated by a plasma actuator in quiescent air.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 34,
Issue. 7,
Zhang, Xin
and
Huang, Yong
2023.
Pulsed Velocity Created by a Plasma Actuator in the Vicinity of the Wall.
AIAA Journal,
Vol. 61,
Issue. 5,
p.
1964.
Hehner, Marc T
Coutinho, Gonçalo
Santos Pereira, Ricardo B
Benard, Nicolas
and
Kriegseis, Jochen
2023.
On the interplay of body-force distributions and flow speed for dielectric-barrier discharge plasma actuators.
Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics,
Vol. 56,
Issue. 37,
p.
375205.
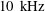 $10~\text{k}\text{Hz}$ discharge frequency to investigate the interplay of the discharge and the surrounding flow. The underlying velocity information for the force estimation is obtained by means of phase-averaged particle image velocimetry; the discharge quantities are determined from a Lissajous-figure analysis. The results uncover a clear cause–effect relation between the phase-dependent effective discharge capacitance of the PA and the resulting spatiotemporal volume-force distributions. From this novel insight, it must be concluded that the instantaneous effective discharge intensity dominates the momentum-transfer rate rather than the formerly assumed operating voltage.
$10~\text{k}\text{Hz}$ discharge frequency to investigate the interplay of the discharge and the surrounding flow. The underlying velocity information for the force estimation is obtained by means of phase-averaged particle image velocimetry; the discharge quantities are determined from a Lissajous-figure analysis. The results uncover a clear cause–effect relation between the phase-dependent effective discharge capacitance of the PA and the resulting spatiotemporal volume-force distributions. From this novel insight, it must be concluded that the instantaneous effective discharge intensity dominates the momentum-transfer rate rather than the formerly assumed operating voltage.