Published online by Cambridge University Press: 16 October 2012
An experiment apparatus has been previously developed with the ability to independently control the instantaneous flow velocity in a water flume. This configuration, which uses two pitching hydrofoils to generate the flow fluctuations, allows the unsteady response of submerged structures to be studied over a wide range of driving frequencies and conditions. Linear unsteady lift theory has been used to calculate the instantaneous circulation about two pitching hydrofoils in uniform flow. A vortex model is then used to describe the circulation in the wakes that determine the velocity perturbations at the centreline between the foils. This paper introduces how the vortex model can be discretized to allow the inverse problem to be solved, such that the foil motions required to recreate a desired velocity time series can be determined. The results of this model are presented for the simplified cases of oscillatory velocity fluctuations in the vertical and stream-wise directions separately, and also simultaneously. The more general case of two-dimensional aperiodic velocity fluctuations is also presented, which demonstrates the capability of configuration between the suggested frequency limits of 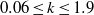 $0. 06\leq k\leq 1. 9$.
$0. 06\leq k\leq 1. 9$.