Article contents
Flexible ring flapping in a uniform flow
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 02 August 2012
Abstract
An improved version of the immersed boundary (IB) method for simulating an initially circular or elliptic flexible ring pinned at one point in a uniform flow has been developed. The boundary of the ring consists of a flexible filament with tension and bending stiffness. A penalty method derived from fluid compressibility was used to ensure the conservation of the internal volume of the flexible ring. At 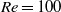 , two different flapping modes were identified by varying the tension coefficient for a fixed bending stiffness, or by changing the bending coefficient for a fixed tension coefficient. The optimal tension and bending coefficients that minimize the drag force of the flexible ring were found. Visualization of the vorticity field showed that the two flapping modes correspond to different vortex shedding patterns. We observed the hysteresis property of the flexible ring, which exhibits bistable states over a range of flow velocities depending on the initial inclination angle, i.e. one is a stationary stable state and the other a self-sustained periodically flapping state. The Reynolds number range of the bistability region and the flapping amplitude were determined for various aspect ratios
, two different flapping modes were identified by varying the tension coefficient for a fixed bending stiffness, or by changing the bending coefficient for a fixed tension coefficient. The optimal tension and bending coefficients that minimize the drag force of the flexible ring were found. Visualization of the vorticity field showed that the two flapping modes correspond to different vortex shedding patterns. We observed the hysteresis property of the flexible ring, which exhibits bistable states over a range of flow velocities depending on the initial inclination angle, i.e. one is a stationary stable state and the other a self-sustained periodically flapping state. The Reynolds number range of the bistability region and the flapping amplitude were determined for various aspect ratios 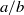 . For
. For 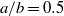 , the hysteresis region arises at the highest Reynolds number and the flapping amplitude in the self-sustained flapping state is minimized. A new bistability phenomenon was observed: for certain aspect ratios, two periodically flapping states coexist with different amplitudes in a particular Reynolds number range, instead of the presence of a stationary stable state and a periodically flapping state.
, the hysteresis region arises at the highest Reynolds number and the flapping amplitude in the self-sustained flapping state is minimized. A new bistability phenomenon was observed: for certain aspect ratios, two periodically flapping states coexist with different amplitudes in a particular Reynolds number range, instead of the presence of a stationary stable state and a periodically flapping state.
- Type
- Papers
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Cambridge University Press 2012
References
- 17
- Cited by


