Article contents
Escaping mass approach for inclined plane and round buoyant jets
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 12 March 2012
Abstract
An integral model predicting the mean flow and mixing properties of inclined plane and round turbulent buoyant jets in a motionless environment of uniform density is proposed. The escaping masses from the main buoyant jet flow are simulated, and the model can be successfully applied to initial discharge inclinations 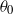 from 90 to
from 90 to 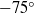 with respect to the horizontal plane. This complementary approach introduces a concentration coefficient, which is calibrated using experimental evidence. The present model has incorporated the second-order approach and, regarding the jet-core region, a jet-core model based on the advanced integral model for the production of more correct transverse profiles of the mean axial velocities and mean concentrations than the common Gaussian or top-hat profiles. The partial differential equations for momentum and tracer conservation are written in orthogonal and cylindrical curvilinear coordinates for inclined plane and round buoyant jets, respectively, and they are integrated under the closure assumptions of (a) quasi-linear spreading of the mean flow and mixing fields, and (b) known transverse profile distributions. The integral forms are solved by employing the Runge–Kutta algorithm. Since the most important contribution in the present model is the simulation of the escaping masses, the model has been called the escaping mass approach (EMA). Herein EMA is applied to predict the mean flow properties (trajectory characteristics, mean axial velocities and mean concentrations) for inclined plane and round buoyant jets. The results predicted are compared with experimental data available in the literature, and the accuracy obtained is more than satisfactory. The performance of the EMA is up to 56 % better than using classical integral procedures. EMA can be used for design purposes and for environmental impact assessment studies.
with respect to the horizontal plane. This complementary approach introduces a concentration coefficient, which is calibrated using experimental evidence. The present model has incorporated the second-order approach and, regarding the jet-core region, a jet-core model based on the advanced integral model for the production of more correct transverse profiles of the mean axial velocities and mean concentrations than the common Gaussian or top-hat profiles. The partial differential equations for momentum and tracer conservation are written in orthogonal and cylindrical curvilinear coordinates for inclined plane and round buoyant jets, respectively, and they are integrated under the closure assumptions of (a) quasi-linear spreading of the mean flow and mixing fields, and (b) known transverse profile distributions. The integral forms are solved by employing the Runge–Kutta algorithm. Since the most important contribution in the present model is the simulation of the escaping masses, the model has been called the escaping mass approach (EMA). Herein EMA is applied to predict the mean flow properties (trajectory characteristics, mean axial velocities and mean concentrations) for inclined plane and round buoyant jets. The results predicted are compared with experimental data available in the literature, and the accuracy obtained is more than satisfactory. The performance of the EMA is up to 56 % better than using classical integral procedures. EMA can be used for design purposes and for environmental impact assessment studies.
JFM classification
- Type
- Papers
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Cambridge University Press 2012
References
- 28
- Cited by


