Published online by Cambridge University Press: 29 August 2012
The structure of viscous and thermal boundary layers at the heated and cooled plates in turbulent thermally driven flows are of fundamental importance for heat transfer and its dependence on the thermal forcing (the Rayleigh number 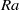 in non-dimensional form). The paper by Shi, Emran & Schumacher (J. Fluid Mech., this issue, vol. 706, 2012, pp. 5–33) stresses the deviations of the boundary layer vertical profiles from the Prandtl–Blasius–Pohlhausen theory. Recent papers showing very similar results, in contrast, focus more on the similarities.
in non-dimensional form). The paper by Shi, Emran & Schumacher (J. Fluid Mech., this issue, vol. 706, 2012, pp. 5–33) stresses the deviations of the boundary layer vertical profiles from the Prandtl–Blasius–Pohlhausen theory. Recent papers showing very similar results, in contrast, focus more on the similarities.