Published online by Cambridge University Press: 30 May 2014
Double-diffusive flux-gradient laws are commonly used to describe the development of large-scale structures driven by salt fingers – thermohaline staircases, collective instability waves and intrusions. The flux-gradient model assumes that the vertical transport is uniquely determined by the local background temperature and salinity gradients. While flux-gradient laws adequately capture mixing characteristics on scales that greatly exceed those of primary double-diffusive instabilities, their accuracy rapidly deteriorates when the scale separation between primary and secondary instabilities is reduced. This study examines conditions for the breakdown of the flux-gradient laws using a combination of analytical arguments and direct numerical simulations. The applicability (failure) of the flux-gradient laws at large (small) scales is illustrated through the example of layering instability, which results in the spontaneous formation of thermohaline staircases from uniform temperature and salinity gradients. Our inquiry is focused on the properties of the ‘point-of-failure’ scale (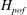 $\def \xmlpi #1{}\def \mathsfbi #1{\boldsymbol {\mathsf {#1}}}\let \le =\leqslant \let \leq =\leqslant \let \ge =\geqslant \let \geq =\geqslant \def \Pr {\mathit {Pr}}\def \Fr {\mathit {Fr}}\def \Rey {\mathit {Re}}H_{pof}$) at which the vertical transport becomes significantly affected by the non-uniformity of the background stratification. It is hypothesized that
$\def \xmlpi #1{}\def \mathsfbi #1{\boldsymbol {\mathsf {#1}}}\let \le =\leqslant \let \leq =\leqslant \let \ge =\geqslant \let \geq =\geqslant \def \Pr {\mathit {Pr}}\def \Fr {\mathit {Fr}}\def \Rey {\mathit {Re}}H_{pof}$) at which the vertical transport becomes significantly affected by the non-uniformity of the background stratification. It is hypothesized that 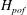 $H_{pof} $ can control some key characteristics of secondary double-diffusive phenomena, such as the thickness of high-gradient interfaces in thermohaline staircases. A more general parametrization of the vertical transport – the flux-gradient-aberrancy law – is proposed, which includes the selective damping of relatively short wavelengths that are inadequately represented by the flux-gradient models. The new formulation is free from the unphysical behaviour of the flux-gradient laws at small scales (e.g. the ultraviolet catastrophe) and can be readily implemented in theoretical and large-scale numerical models of double-diffusive convection.
$H_{pof} $ can control some key characteristics of secondary double-diffusive phenomena, such as the thickness of high-gradient interfaces in thermohaline staircases. A more general parametrization of the vertical transport – the flux-gradient-aberrancy law – is proposed, which includes the selective damping of relatively short wavelengths that are inadequately represented by the flux-gradient models. The new formulation is free from the unphysical behaviour of the flux-gradient laws at small scales (e.g. the ultraviolet catastrophe) and can be readily implemented in theoretical and large-scale numerical models of double-diffusive convection.