Published online by Cambridge University Press: 09 July 2019
In an annular spherical domain with separation 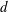 $d$, the onset of convective motion occurs at a critical Rayleigh number
$d$, the onset of convective motion occurs at a critical Rayleigh number 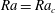 $Ra=Ra_{c}$. Solving the axisymmetric linear stability problem shows that degenerate points
$Ra=Ra_{c}$. Solving the axisymmetric linear stability problem shows that degenerate points 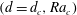 $(d=d_{c},Ra_{c})$ exist where two modes simultaneously become unstable. Considering the weakly nonlinear evolution of these two modes, it is found that spatial resonances play a crucial role in determining the preferred convection pattern for neighbouring modes
$(d=d_{c},Ra_{c})$ exist where two modes simultaneously become unstable. Considering the weakly nonlinear evolution of these two modes, it is found that spatial resonances play a crucial role in determining the preferred convection pattern for neighbouring modes  $(\ell ,\ell \pm 1)$ and non-neighbouring even modes
$(\ell ,\ell \pm 1)$ and non-neighbouring even modes 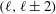 $(\ell ,\ell \pm 2)$. Deriving coupled amplitude equations relevant to all degeneracies, we outline the possible solutions and the influence of changes in
$(\ell ,\ell \pm 2)$. Deriving coupled amplitude equations relevant to all degeneracies, we outline the possible solutions and the influence of changes in 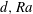 $d,Ra$ and Prandtl number
$d,Ra$ and Prandtl number 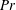 $Pr$. Using direct numerical simulation (DNS) to verify all results, time periodic solutions are also outlined for small
$Pr$. Using direct numerical simulation (DNS) to verify all results, time periodic solutions are also outlined for small  $Pr$. The
$Pr$. The 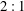 $2:1$ periodic signature observed to be general for oscillations in a spherical annulus is explained using the structure of the equations. The relevance of all solutions presented is determined by computing their stability with respect to non-axisymmetric perturbations at large
$2:1$ periodic signature observed to be general for oscillations in a spherical annulus is explained using the structure of the equations. The relevance of all solutions presented is determined by computing their stability with respect to non-axisymmetric perturbations at large  $Pr$.
$Pr$.
DNS of the odd-odd $\ell=1, m=3$ periodic solution for $\mathrm{Ra}_c = 440.852, \epsilon =5.85$ and $\Pran = 0.05$. Even and odd mode components of the solution oscillate with their frequencies in a $2:1$ ratio.