Article contents
Scaling laws for drag-to-thrust transition and propulsive performance in pitching flexible plates
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 27 April 2022
Abstract
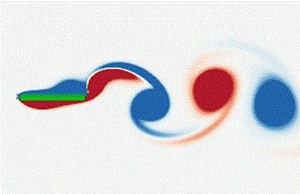
The propulsion of a pitching flexible plate in a uniform flow is investigated numerically. The effects of bending stiffness ( $K$), pitching amplitude (
$K$), pitching amplitude ( $A_L$) and frequency (
$A_L$) and frequency ( $St$) on the wake patterns, thrust generations and propulsive performances of the fluid–plate system are analysed. Four typical wake patterns, i.e. von Kármán, reversed von Kármán, deflected and chaotic wakes, emerge from various kinematics, and the
$St$) on the wake patterns, thrust generations and propulsive performances of the fluid–plate system are analysed. Four typical wake patterns, i.e. von Kármán, reversed von Kármán, deflected and chaotic wakes, emerge from various kinematics, and the  $St-A_L$ wake maps are given for various
$St-A_L$ wake maps are given for various  $K$. The drag-to-thrust transitions (DTT) and the wake transitions (WT) between the von Kármán and reversed von Kármán wakes are examined. Results indicate that the WT and DTT boundaries can be scaled by the chord-averaged distance of travel,
$K$. The drag-to-thrust transitions (DTT) and the wake transitions (WT) between the von Kármán and reversed von Kármán wakes are examined. Results indicate that the WT and DTT boundaries can be scaled by the chord-averaged distance of travel,  $\mathcal {L}$, which leads to
$\mathcal {L}$, which leads to  $\mathcal {L}\times St \approx 1$ and
$\mathcal {L}\times St \approx 1$ and  $\mathcal {L}\times St \approx 1.2$, respectively. Further, the resonance mechanism for the performance enhancement is revealed and confirmed in a wide range of parameters. The dimensionless average speed of plate,
$\mathcal {L}\times St \approx 1.2$, respectively. Further, the resonance mechanism for the performance enhancement is revealed and confirmed in a wide range of parameters. The dimensionless average speed of plate,  $\mathcal {U^*}\left (=\mathcal {L}\times St\right )$, is adopted merely to characterize the propulsive performances. For the first time, the
$\mathcal {U^*}\left (=\mathcal {L}\times St\right )$, is adopted merely to characterize the propulsive performances. For the first time, the  $\mathcal {U^*}$-based scaling laws for the thrust and power are revealed in pitching rigid and flexible plates for various
$\mathcal {U^*}$-based scaling laws for the thrust and power are revealed in pitching rigid and flexible plates for various  $A_L$ and
$A_L$ and  $St$. This study may deepen our understanding of biological swimming and flying, and provide a guide for bionic design.
$St$. This study may deepen our understanding of biological swimming and flying, and provide a guide for bionic design.
JFM classification
- Type
- JFM Rapids
- Information
- Copyright
- © The Author(s), 2022. Published by Cambridge University Press
References
REFERENCES
- 8
- Cited by



