Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Adell, José A.
and
Sangüesa, Carmen
1999.
Direct and converse inequalities for positive linear operators on the positive semi-axis.
Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series A. Pure Mathematics and Statistics,
Vol. 66,
Issue. 1,
p.
90.
Sangüesa, C.
2008.
Error bounds in approximations of random sums using gamma-type operators.
Insurance: Mathematics and Economics,
Vol. 42,
Issue. 2,
p.
484.
Sangüesa, Carmen
2010.
Uniform error bounds for a continuous approximation of non-negative random variables.
Bernoulli,
Vol. 16,
Issue. 2,
Sangüesa, C.
2011.
On the approximation of functions satisfying defective renewal equations.
Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics,
Vol. 236,
Issue. 6,
p.
1042.
Mazziotta, Adriano
Vizentin-Bugoni, Jeferson
Tøttrup, Anders P.
Bruun, Hans Henrik
Fritz, Örjan
and
Heilmann-Clausen, Jacob
2017.
Interaction type and intimacy structure networks between forest-dwelling organisms and their host trees.
Basic and Applied Ecology,
Vol. 24,
Issue. ,
p.
86.
Alai, Daniel H.
2019.
Multivariate lifetime distributions for the exponential dispersion family.
Scandinavian Actuarial Journal,
Vol. 2019,
Issue. 5,
p.
387.
McVinish, R.
Lester, R. J. G.
and
Yaro, Clement Ameh
2024.
A graphical exploration of the relationship between parasite aggregation indices.
PLOS ONE,
Vol. 19,
Issue. 12,
p.
e0315756.
Germain, Gilles
and
Swan, Yvik
2025.
Bounding the $$L^1$$-Distance Between One-Dimensional Continuous and Discrete Distributions via Stein’s Method.
Journal of Theoretical Probability,
Vol. 38,
Issue. 1,
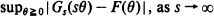 . In particular, we show that the exact order of uniform convergence is s–p, where p = min(1, α). Various kinds of applications concerning charged multiplicity distributions, the Yule birth process and Bernstein-type operators are also given.
. In particular, we show that the exact order of uniform convergence is s–p, where p = min(1, α). Various kinds of applications concerning charged multiplicity distributions, the Yule birth process and Bernstein-type operators are also given.