No CrossRef data available.
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 04 January 2023
We present a Markov chain example where non-reversibility and an added edge jointly improve mixing time. When a random edge is added to a cycle of n vertices and a Markov chain with a drift is introduced, we get a mixing time of
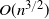 $O(n^{3/2})$
with probability bounded away from 0. If only one of the two modifications were performed, the mixing time would stay
$O(n^{3/2})$
with probability bounded away from 0. If only one of the two modifications were performed, the mixing time would stay
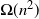 $\Omega(n^2)$
.
$\Omega(n^2)$
.