Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by Crossref.
Weil, Wolfgang
1983.
Convexity and Its Applications.
p.
360.
Miles, R. E.
1985.
A comprehensive set of stereological formulae for embedded aggregates of not‐necessarily‐convex particles.
Journal of Microscopy,
Vol. 138,
Issue. 2,
p.
115.
Jensen, E. B.
and
Gundersen, H. J. G.
1985.
The stereological estimation of moments of particle volume.
Journal of Applied Probability,
Vol. 22,
Issue. 01,
p.
82.
Gundersen, H. J. G.
and
Jensen, E. B.
1985.
Stereological estimation of the volume‐weighted mean volume of arbitrary particles observed on random sections*.
Journal of Microscopy,
Vol. 138,
Issue. 2,
p.
127.
Gundersen, H. J. G.
1986.
Stereology of arbitrary particles*.
Journal of Microscopy,
Vol. 143,
Issue. 1,
p.
3.
Kellerer, A. M.
1986.
The variance of a Poisson process of domains.
Journal of Applied Probability,
Vol. 23,
Issue. 2,
p.
307.
Gundersen, H. J. G.
1988.
The nucleator.
Journal of Microscopy,
Vol. 151,
Issue. 1,
p.
3.
Jensen, E. B.
and
Gundersen, H. J. G.
1989.
Fundamental stereological formulae based on isotropically orientated probes through fixed points with applications to particle analysis.
Journal of Microscopy,
Vol. 153,
Issue. 3,
p.
249.
Hazewinkel, M.
1990.
Encyclopaedia of Mathematics.
p.
1.
SCHNEIDER, Rolf
and
WIEACKER, John A.
1993.
Handbook of Convex Geometry.
p.
1349.
Kuz’min, L. V.
Fofanova, T. S.
Tsalenko, M. Sh.
Ivanov, A. B.
Popov, V. L.
Shevrin, L. N.
Grishin, V. N.
Lavrent’ev, M. M.
Soltan, P. S.
Nagornyĭ, N. M.
Bokut’, L. A.
Nikol’skiĭ, S. M.
Chernavskiĭ, A. V.
Shefel’, S. Z.
Dragalin, A. G.
Dushskiĭ, V. A.
Sobolev, S. K.
Plisko, V. E.
Kudryavtsev, L. D.
Danilov, V. I.
Trenogin, V. A.
Vil’yams, N. N.
Voĭtsekhovskiĭ, M. I.
Tarakanov, V. E.
Rukova, S. A.
Pagurova, V. I.
Ostrovskiĭ, I. V.
Shtern, A. I.
Prokhorov, Yu. V.
Anosov, D. V.
Stepanov, S. A.
Shubin, M. A.
Zaĭtsev, V. I.
Nikulin, M. S.
Sokolov, D. D.
Zhelobenko, D. P.
Naĭmark, M. A.
Pasynkov, B. A.
Yanovskaya, E. B.
Solomentsev, E. D.
Tamrazov, P. M.
Lumiste, Ü.
Kolmogorov, A. N.
Chentsov, N. N.
Dobrushin, R. L.
Prelov, V. V.
Prokhorov, A. V.
Vrublevskaya, I. N.
Tikhomirov, V. M.
Mikhalev, A. V.
Tuganbaev, A. A.
Dolgachev, I. V.
Gol’shteĭn, E. G.
Levner, E. V.
Il’in, V. A.
Ladis, N. N.
Khvedelidze, B. V.
Duduchava, R. V.
Arsenin, V. Ya.
Filippov, A. F.
Shushurin, S. F.
Samoĭlenko, A. M.
Rozov, N. Kh.
Minlos, R. A.
Bredikhin, B. M.
Malyshev, A. V.
Davydov, Yu. M.
Millonshchikov, V. M.
Brychkov, Yu. A.
Prudnikov, A. P.
Soldatov, A. P.
Chaernavakiĭ, A. V.
Bol’shev, L. N.
Ponomarev, V. I.
Rozhdestvenskiĭ, B. L.
Burago, Yu. D.
Zorich, V. A.
Kulikov, Vik. S.
Sretenskiĭ, L. N.
Kaz’min, Yu. A.
Samarin, M. K.
Yanovich, L. A.
Kreĭn, S. G.
Subbotin, Yu. N.
Sudorov, Yu. V.
Semenov, A. L.
Sklyarenko, E. G.
Pospelov, V. V.
Sazonov, V. V.
Dezin, A. A.
Wing, G. M.
Alekseevskiĭ, D. V.
Sobolev, V. I.
Mikheev, V. M.
Ikramov, Kh. D.
Iskovskikh, V. A.
Ponomarev, D. A.
Arkhangel’skiĭ, A. V.
Merzlyakov, Yu. I.
Dem’yanenko, V. A.
Il’yashenko, Yu. S.
Millionshchikov, V. M.
Mal’tsev, A. A.
Zalgaller, V. A.
Ivanova, O. A.
Fomenko, V. T.
Smirnov, D. M.
Vapnyarskiĭ, I. B.
Sabitov, I. Kh.
Shtan’ko, M. A.
Onishchik, A. L.
Lebedev, V. I.
Novikov, A. A.
Fedenko, A. S.
Tikhonov, A. N.
Kuptsov, L. P.
Volkov, I. I.
Bityutskov, V. I.
Remeslennikov, V. N.
Shiryaev, A. N.
Lukashenko, T. P.
Kukin, V. D.
Sirota, S. M.
Sidorov, Yu. V.
Aleksandrov, I. A.
and
Skornyakov, L. A.
1995.
Encyclopaedia of Mathematics.
p.
123.
Jensen, Eva B. Vedel
1995.
Rotational versions of the Crofton formula.
Advances in Applied Probability,
Vol. 27,
Issue. 1,
p.
87.
Cabo, A. J.
and
Baddeley, A. J.
1995.
Line transects, covariance functions and set convergence.
Advances in Applied Probability,
Vol. 27,
Issue. 3,
p.
585.
Hamprecht, Markus
1996.
Controlling von Konzernplanungssytemen.
p.
159.
Gardner, R.J.
2007.
The dual Brunn–Minkowski theory for bounded Borel sets: Dual affine quermassintegrals and inequalities.
Advances in Mathematics,
Vol. 216,
Issue. 1,
p.
358.
Kiderlen, Markus
2013.
Stochastic Geometry, Spatial Statistics and Random Fields.
Vol. 2068,
Issue. ,
p.
21.
2014.
Mathematical Foundations of Image Processing and Analysis 2.
p.
349.
2014.
Mathematical Foundations of Image Processing and Analysis 1.
p.
309.
2014.
Journal of Applied Probability Volume 51 (2014): Index.
Journal of Applied Probability,
Vol. 51,
Issue. 4,
p.
1196.
Lv, Songjun
2024.
Sharp norm estimates for functional dual affine quermassintegrals.
Banach Journal of Mathematical Analysis,
Vol. 18,
Issue. 2,


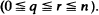 Stochastic applications in
Stochastic applications in 