Published online by Cambridge University Press: 16 July 2020
If we pick n random points uniformly in 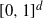 $[0,1]^d$
and connect each point to its
$[0,1]^d$
and connect each point to its 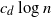 $c_d \log{n}$
nearest neighbors, where
$c_d \log{n}$
nearest neighbors, where 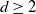 $d\ge 2$
is the dimension and
$d\ge 2$
is the dimension and 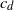 $c_d$
is a constant depending on the dimension, then it is well known that the graph is connected with high probability. We prove that it suffices to connect every point to
$c_d$
is a constant depending on the dimension, then it is well known that the graph is connected with high probability. We prove that it suffices to connect every point to 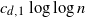 $ c_{d,1} \log{\log{n}}$
points chosen randomly among its
$ c_{d,1} \log{\log{n}}$
points chosen randomly among its 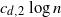 $ c_{d,2} \log{n}$
nearest neighbors to ensure a giant component of size
$ c_{d,2} \log{n}$
nearest neighbors to ensure a giant component of size 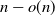 $n - o(n)$
with high probability. This construction yields a much sparser random graph with
$n - o(n)$
with high probability. This construction yields a much sparser random graph with 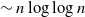 $\sim n \log\log{n}$
instead of
$\sim n \log\log{n}$
instead of 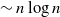 $\sim n \log{n}$
edges that has comparable connectivity properties. This result has non-trivial implications for problems in data science where an affinity matrix is constructed: instead of connecting each point to its k nearest neighbors, one can often pick
$\sim n \log{n}$
edges that has comparable connectivity properties. This result has non-trivial implications for problems in data science where an affinity matrix is constructed: instead of connecting each point to its k nearest neighbors, one can often pick 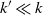 $k'\ll k$
random points out of the k nearest neighbors and only connect to those without sacrificing quality of results. This approach can simplify and accelerate computation; we illustrate this with experimental results in spectral clustering of large-scale datasets.
$k'\ll k$
random points out of the k nearest neighbors and only connect to those without sacrificing quality of results. This approach can simplify and accelerate computation; we illustrate this with experimental results in spectral clustering of large-scale datasets.