No CrossRef data available.
Article contents
Jovian magnetospheric and auroral effects of the SL9 impacts
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 02 August 2016
Abstract
The collisions of comet Shoemaker-Levy 9 with Jupiter have produced many surprising auroral and magnetospheric phenomena. The energy released during the passage of the cometary dust comas through the jovian magnetosphere and at atmospheric explosion could lead to impulsive particle acceleration, enhanced radial diffusive transport, and the establishment of field-aligned current systems connecting the comet impact sites to their respective magnetic conjugate points. Some of the observed effects such as the abrupt increase of decimetric radio emission, the excitation of infrared 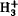 emissions and mid-latitude auroral emission in the ultraviolet, could be interpreted within the framework of these mechanisms. Several auroral features like the X-ray outbursts and short-term variations in the UV emissions are more puzzling and require further observation of jovian auroral dynamics in these wavelength ranges in coordination with the Galileo mission.
emissions and mid-latitude auroral emission in the ultraviolet, could be interpreted within the framework of these mechanisms. Several auroral features like the X-ray outbursts and short-term variations in the UV emissions are more puzzling and require further observation of jovian auroral dynamics in these wavelength ranges in coordination with the Galileo mission.
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- International Astronomical Union Colloquium , Volume 156: The Collision of Comet Shoemaker-Levy 9 and Jupiter , May 1996 , pp. 347 - 373
- Copyright
- Copyright © Cambridge University Press 1996


