Article contents
Dissociation Energies and Partition Functions of Small Molecules
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 12 April 2016
Extract
For a simple dissociation equilibrium

the equilibrium constant Kp at temperature T can be written in terms of partial pressures p or densities n in the form given by Equation 6 of Tatum (1966)
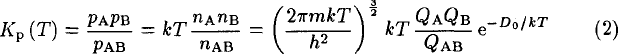
where m is the reduced mass of AB, k the Boltzmann constant, h the Planck constant, QA, QB, QAB the internal partition functions of the species, and D0 the dissociation energy of AB. This equation derives from a more general expression of Kp (T) for a chemical reaction that is demonstrated in all physicalchemistry textbooks treating statistical thermodynamics (see for example Atkins 1990). Partition functions are weighted Boltzmann factors

with ϵn corresponding to the energy of the eigenstates of degeneracy gn. Provided all the eigenvalues are known, Q values can be calculated exactly. Derivations and calculations of the partition functions can be found in textbooks or in reviews relating to astrophysics.
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- International Astronomical Union Colloquium , Volume 146: Molecules in the Stellar Environment , 1994 , pp. 250 - 264
- Copyright
- Copyright © Springer-Verlag 1994
References
- 2
- Cited by


