Published online by Cambridge University Press: 10 March 2021
We construct a calculus of functors in the spirit of orthogonal calculus, which is designed to study ‘functors with reality’ such as the Real classifying space functor, 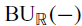 . The calculus produces a Taylor tower, the n-th layer of which is classified by a spectrum with an action of
. The calculus produces a Taylor tower, the n-th layer of which is classified by a spectrum with an action of 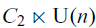 . We further give model categorical considerations, producing a zigzag of Quillen equivalences between spectra with an action of
. We further give model categorical considerations, producing a zigzag of Quillen equivalences between spectra with an action of 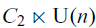 and a model structure on the category of input functors which captures the homotopy theory of the n-th layer of the Taylor tower.
and a model structure on the category of input functors which captures the homotopy theory of the n-th layer of the Taylor tower.
The author wishes to thank David Barnes for numerous helpful and insightful conversations and suggestions on this material.