No CrossRef data available.
Article contents
VII.—On some Physical Changes in the Earth's Crust
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 01 May 2009
Extract
Subterranean landslips differ from landslips occurring in cliffs along the coast, and in escarpments elsewhere, in that, a fissure having been formed and its sides become separated (Figs. 2 and 3 a), so that they are without support along the line of division, 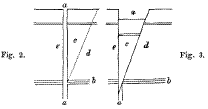 it may happen that by the giving way of some soft or unconsolidated stratum (b), at any depth, from a few feet only, down to the molten nucleus, wedge-shaped masses (c) extending parallel to the fissure would break off (d) and slipping down strike against the opposite wall (Fig. 3e) and thus fill up the fissure.
it may happen that by the giving way of some soft or unconsolidated stratum (b), at any depth, from a few feet only, down to the molten nucleus, wedge-shaped masses (c) extending parallel to the fissure would break off (d) and slipping down strike against the opposite wall (Fig. 3e) and thus fill up the fissure.
- Type
- Original Articles
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Cambridge University Press 1889
References
page 116 note 1 Proc. Liverpool Geological Society. An abstract of this Essay (“On Fissures, Faults, Contortion and Cleavage,” by Ricketts, Charles) appeared in the Geological Magazine, Vol. X. 1873, p. 202.CrossRefGoogle Scholar
page 116 note 2 Nature, vol. xii. p. 93.Google Scholar
page 116 note 3 Brit. Assoc. Report, 1881, p. 201.Google Scholar
page 116 note 4 Earthquakes and other Earth Movements, by Milne, John, F.G.S., 1886, p. 279.Google Scholar
page 116 note 5 Nature, vol. xxiii. 1881, p. 498.Google Scholar
page 116 note 6 Nature, vol. xxix. 1883, p. 45.Google Scholar
page 117 note 1 Principles of Geology, vol. ii. chap. xxviii.–xxx.
page 117 note 2 Report of the Royal Society of London to investigate the great Neapolitan earthquake of 1857.
page 117 note 3 Memoirs of Geol. Survey of India; vol. xix.; also Quart. Journ. Geol. Soc. vol. xxviii. p. 255.Google Scholar
page 117 note 4 Quart. Journ. Geol. Soc. vol. vi. p. xlii.Google Scholar
page 117 note 5 Origin of Mountain Ranges, p. 125.Google Scholar
page 118 note 1 Phil. Mag. Jan. 1888; see also for Nov. 1887.
page 119 note 1 Quart. Journ. Geol. Soc. vol. vi. p. lxiii.Google Scholar
page 119 note 2 They are copied in “Nature,” vol. xix. 12 5, 1878, p. 103.Google Scholar The Rev. Osmond Fisher has reproduced one in “Physics of the Earth's Crust,” p. 128,Google Scholar but does not coincide with the deduction Prof. Favre draws from the experiments.


