Article contents
A genetic study of primary and secondary reversions of some tryptophanA auxotrophs of Salmonella typhimurium
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 14 April 2009
Extract
1. The linkage order of four tryA mutants of S. typhimurium, and cysB-12, is:
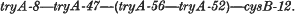
Attempts to plot the position of tryA-50 were unsuccessful.
2. Some of the reversions of tryA-8, tryA-47, tryA-56 and tryA-50 were analysed genetically; tryA-52 does not revert. All four auxotrophs gave reversions that were phenotypically and genetically indistinguishable from that expected by back-mutation of the original mutant site.
3. Both tryA-8 and tryA-50 produced reversions that grew as wild-type but were due to unlinked suppressor mutations. Some of these were super-suppressors in that they suppressed both tryA-8 and tryB-4; others suppressed many site mutants in the tryA gene but did not suppress tryB-4.
4. All the slow-growing reversions of tryA-8, tryA-50 and tryA-56, and a minority of the semi-fast reversions of tryA-8, were due to unlinked suppressors.
5. All the slow-growing reversions of tryA-47, the semi-fast reversions of tryA-56 and the majority of the semi-fast reversions of tryA-8 were due to genetic changes that were inseparable, in very extensive experiments, from their original mutant site.
6. Slow-growing reversions of tryA-47 produced faster growing mutants. Some of these were due to mutation in unlinked modifying genes and in others the genetic change was within the tryA gene. Nine of the latter had the genetic change just to the left of the 47S site; in one the change was inseparable from the 47S site. None had this further change to the right of the 47S site. These further changes, in the absence of the 47S site, gave prototrophic phenotypes; they are inter-site suppressors.
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Cambridge University Press 1967
References
REFERENCES
- 4
- Cited by


