Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Korol, Abraham B
Ronin, Yefim I
and
Nevo, Eviatar
1998.
Approximate Analysis of QTL-Environment Interaction with No Limits on the Number of Environments.
Genetics,
Vol. 148,
Issue. 4,
p.
2015.
Korol, A B
Ronin, Y I
Nevo, E
and
Hayes, P M
1998.
Multi-interval mapping of correlated trait complexes.
Heredity,
Vol. 80,
Issue. 3,
p.
273.
Korol, Abraham B
Ronin, Yefim I
Itskovich, Alexander M
Peng, Junhua
and
Nevo, Eviatar
2001.
Enhanced Efficiency of Quantitative Trait Loci Mapping Analysis Based on Multivariate Complexes of Quantitative Traits.
Genetics,
Vol. 157,
Issue. 4,
p.
1789.
Lichtenzveig, Judith
Bonfil, David J.
Zhang, Hong-Bin
Shtienberg, Dani
and
Abbo, Shahal
2006.
Mapping quantitative trait loci in chickpea associated with time to flowering and resistance to Didymella rabiei the causal agent of Ascochyta blight.
Theoretical and Applied Genetics,
Vol. 113,
Issue. 7,
p.
1357.
Rae, Anne M
Street, Nathaniel Robert
Robinson, Kathryn Megan
Harris, Nicole
and
Taylor, Gail
2009.
Five QTL hotspots for yield in short rotation coppice bioenergy poplar: The Poplar Biomass Loci.
BMC Plant Biology,
Vol. 9,
Issue. 1,
Korol, Abraham
Mester, David
Frenkel, Zeev
and
Ronin, Yefim
2009.
Genetics and Genomics of the Triticeae.
p.
163.
Korol, Abraham
Frenkel, Zeev
Orion, Ori
and
Ronin, Yefim
2012.
Some ways to improve QTL mapping accuracy.
Animal Genetics,
Vol. 43,
Issue. s1,
p.
36.
Hübner, S.
Bdolach, E.
Ein‐Gedy, S.
Schmid, K. J.
Korol, A.
and
Fridman, E.
2013.
Phenotypic landscapes: phenological patterns in wild and cultivated barley.
Journal of Evolutionary Biology,
Vol. 26,
Issue. 1,
p.
163.
Kamphuis, Lars G.
Lichtenzveig, Judith
Peng, Kefan
Guo, Su-Min
Klingler, John P.
Siddique, Kadambot H. M.
Gao, Ling-Ling
and
Singh, Karam B.
2013.
Characterization and genetic dissection of resistance to spotted alfalfa aphid (Therioaphis trifolii) in Medicago truncatula.
Journal of Experimental Botany,
Vol. 64,
Issue. 16,
p.
5157.
Liu, Guanfu
Li, Pengfei
Liu, Yukun
and
Pu, Xiaolong
2020.
Hypothesis testing for quantitative trait locus effects in both location and scale in genetic backcross studies.
Scandinavian Journal of Statistics,
Vol. 47,
Issue. 4,
p.
1064.
Ren, Pengcheng
Liu, Guanfu
Pu, Xiaolong
and
Li, Yan
2022.
Generalized fiducial methods for testing quantitative trait locus effects in genetic backcross studies.
Statistical Theory and Related Fields,
Vol. 6,
Issue. 2,
p.
148.
Liu, Guanfu
and
Hu, Zongliang
2023.
Testing quantitative trait locus effects in genetic backcross studies with double recombination occurring.
Journal of Applied Statistics,
Vol. 50,
Issue. 4,
p.
927.
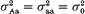 and (ii)
and (ii) 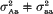 . It was found that, if the variance effect of A/a is large enough, then in spite of the necessity to evaluate an increased number of parameters, the more correctly specified model provides an increase in the resolution power, as compared to the situation (i). This is not unexpected, if either
. It was found that, if the variance effect of A/a is large enough, then in spite of the necessity to evaluate an increased number of parameters, the more correctly specified model provides an increase in the resolution power, as compared to the situation (i). This is not unexpected, if either 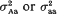 in (ii) is lower than
in (ii) is lower than 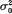 from (i). But our conclusion holds even if
from (i). But our conclusion holds even if 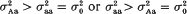 . These advantages are illustrated on sweet corn data data (F3 families of F2 genotypes). In particular, the log-likelihood test statistics and the parameter estimates obtained for a QT locus in the distal region of chromosome 2 show that the allele enhancing the trait is recessive over the opposite allele simultaneously for the mean value and variance.
. These advantages are illustrated on sweet corn data data (F3 families of F2 genotypes). In particular, the log-likelihood test statistics and the parameter estimates obtained for a QT locus in the distal region of chromosome 2 show that the allele enhancing the trait is recessive over the opposite allele simultaneously for the mean value and variance.