Article contents
Dislodgement and thymineless elimination of N-group plasmids
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 14 April 2009
Summary
Thymineless strains of Escherichia coli C600 were constructred harbouring both an R factor of the N incompatibility group (R46 or R447b) and a compatible plasmid (Plac-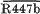 of the A-C group or the Iα plasmid R62), which contained a segment of N group DNA. Selection was made for the transferred plasmid and dislodgement phenomena were manifest either as loss of an entire plasmid or as deletions of a region of plasmid DNA. Even after the two R factors had become established as separate replicons, the N group R factor but not the other plasmid exhibited instability.
of the A-C group or the Iα plasmid R62), which contained a segment of N group DNA. Selection was made for the transferred plasmid and dislodgement phenomena were manifest either as loss of an entire plasmid or as deletions of a region of plasmid DNA. Even after the two R factors had become established as separate replicons, the N group R factor but not the other plasmid exhibited instability.
Thymine starvation of strain C600 thy (R447b/R62) increased the elimination rate of the N group plasmid R447b but no elimination of R62 was observed. However, thymine starvation of strain C600 thy (R46/Plac-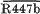 ) not only increased the rate of elimination of R46 but also increased the rate of loss of Plac-
) not only increased the rate of elimination of R46 but also increased the rate of loss of Plac-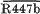 . There was no detectable increase in nuclease activity in unstarved R46/Plac-
. There was no detectable increase in nuclease activity in unstarved R46/Plac-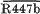 strains and it is concluded that dislodgement of R46 from these strains is not due to induction of the nuclease that has been proposed to be responsible for the elimination of N group plasmids during thymine starvation.
strains and it is concluded that dislodgement of R46 from these strains is not due to induction of the nuclease that has been proposed to be responsible for the elimination of N group plasmids during thymine starvation.
Two variants of Plac-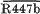 were isolated. These did not dislodge R46 from unstarved R46/Plac-
were isolated. These did not dislodge R46 from unstarved R46/Plac-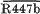 strains and were not lost during thymine starvation even though thymineless elimination of R46 occurred at normal frequency.
strains and were not lost during thymine starvation even though thymineless elimination of R46 occurred at normal frequency.
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Cambridge University Press 1977
References
REFERENCES
- 2
- Cited by


