No CrossRef data available.
Article contents
PW01-261 - Betahistine (HistaleantTM) Safely Mitigates Olanzapine Induced Weight Gain
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 17 April 2020
Abstract
Patients treated with olanzapine may experience substantial weight gain. This may result in metabolic abnormalities and contributes to lack of compliance. Recent findings indicate that the weight gain associated with Olanzapine is mediated by hypothalamic blockade of the Histamine H1 Receptor. Betahistine (Histalean™) is a centrally acting Histamine 1 receptor agonist used for the treatment of vertigo. We herein report the effect of Betahistine on Olanzapine induced weight gain.
To evaluate the safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics of this drug combination.
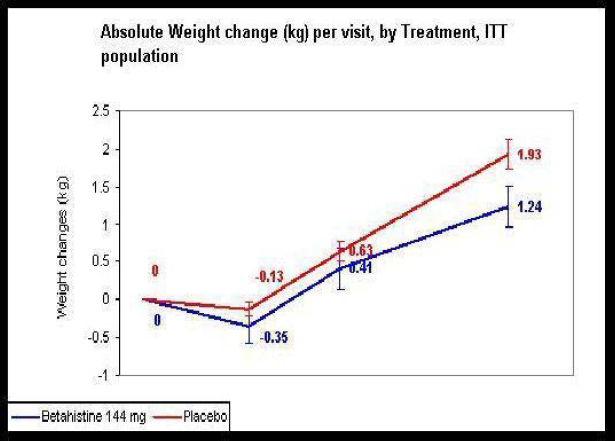
48 healthy women were randomized in a double blinded manner to receive Betahistine 144 mg/day or matching placebo. One week later, all subjects began 3 weeks Olnazapine (7.5 mg or 10 mg/day) treatment period.
Overall the combined treatment was well tolerated. No difference was observed between treatment and placebo groups in adverse events rate or type. In the ITT population, the average weight gain in the Betahistine group was 1.2±1.3 Kg and 1.9 ± 0.9 Kg in the placebo group (p=0.0489). 52% of the placebo group gained more than 2.0 Kg versus only 23% in the treatment group (p= 0.043).
These results indicate that Betahistine is safe and effective in preventing Olanzapine associated weight gain.
[Absolute Weight change (kg) per visit, by Treatmen]
- Type
- Psychopharmacological treatment and biological therapies
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © European Psychiatric Association 2009



Comments
No Comments have been published for this article.