No CrossRef data available.
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 19 July 2023
Major Depressive Disorder (MDD) is associated with high mortality, disability and morbidity. Studies demonstrated mixed results on effects of depression treatments on quality of life (QOL).
To evaluate the severity of depression among Jordanian patients diagnosed with MDD before and after treatment and to find any relationship between QOL, depression severity and perceived cognitive dysfunction.
Patients from both genders, 18-65 years old and diagnosed with MDD were included to attend two visits; at baseline and 6 weeks after treatment, in each they completed three questionnaires: Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ-9) for depression severity, patient-rated Perceived Deficit Questionnaire (PDQ-5) for cognitive function, and World Health Organization Quality of Life Brief (WHOQOL-BREF) format.
A total of 92 patients completed the study. The scores of the different questionnaires and their correlations before and after treatment are presented in tables 1 and 2. Correlations between PHQ-9 and PDQ-5 before and after treatment are illustrated in figs 1 and 2, respectively.Table 1:
Total scores for WHOQOL-BREF format, PDQ-5 and PHQ-9, before and after treatment
| Questionnaire | Before | After | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| General quality of life | 2.5±1 | 3.5±0.7 | <0.0001 |
| General health satisfaction | 2.3±1 | 3.4±0.9 | <0.0001 |
| Physical health (Domain 1) | 10±2.6 | 13.9±2.6 | <0.0001 |
| Psychological (Domain 2) | 8±2.3 | 12.6±2.3 | <0.0001 |
| Social relationships (Domain 3) | 9±3.2 | 12.8±2.8 | <0.0001 |
| Environment (Domain 4) | 12.3±3 | 14.4±7.5 | 0.0003 |
| Patient-rated Perceived Deficit 5 (PDQ-5) | 13±4.4 | 7.2±4 | <0.0001 |
| Patient health questionnaire 9 (PHQ-9) | 19±5.4 | 7.1±5.1 | <0.0001 |
Values are presented as mean±SD. Analysis: Paired t test. P<0.05 is significant.
Table 2:Correlations between total scores for all of the domains for WHOQOL-BREF and PDQ-5, and between WHOQOL-BREF and PHQ-9, before and after treatment
| Domains/Facets | Patient-rated Perceived Deficit 5 (PDQ-5) | Patient health questionnaire 9 (PHQ-9) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before (r, p) | After (r, p) | Before (r, p) | After (r, p) | |
| General quality of life | -0.38, 0.0001 | -0.26, 0.01 | -0.55, <0.0001 | -0.49, <0.0001 |
| General health satisfaction | -0.24, 0.02 | -0.14, 0.2 | -0.51, <0.0001 | -0.48, <0.0001 |
| Physical health (Domain 1) | -0.37, 0.0003 | -0.50, <0.0001 | -0.57, <0.0001 | -0.76, <0.0001 |
| Psychological (Domain 2) | -0.46, <0.0001 | -0.43, <0.0001 | -0.58, <0.0001 | -0.68, <0.0001 |
| Social relationships (Domain 3 | -0.37, 0.0002 | -0.37, 0.0002 | -0.42, <0.0001 | -0.40, <0.0001 |
| Environment (Domain 4) | -0.52, <0.0001 | -0.21, 0.047 | -0.36, 0.0004 | -0.12, 0.2 |
Spearman correlation (r); P<0.05 is significant. WHOQOL: World Health Organization Quality of Life.
Image:
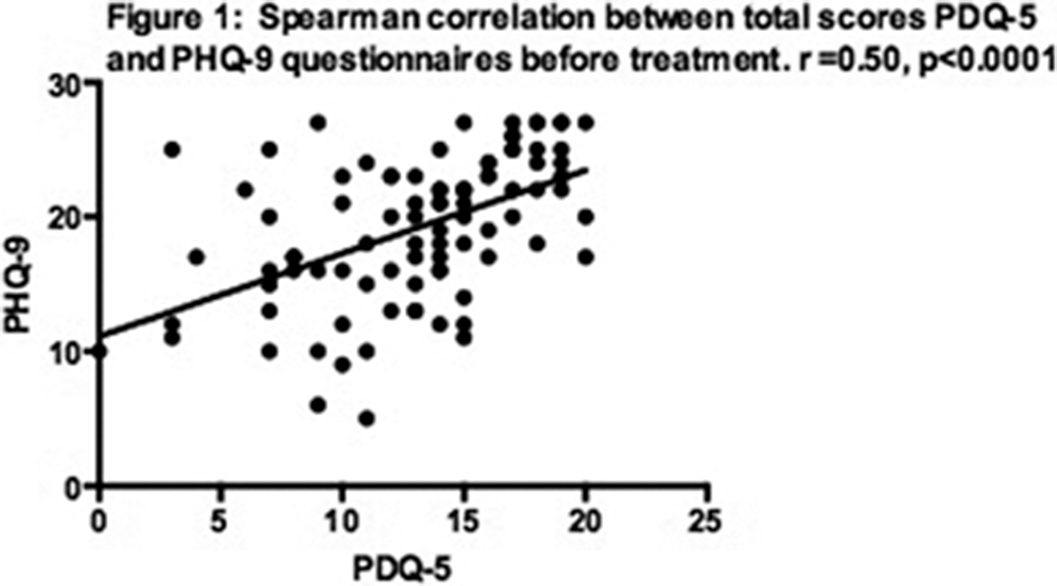
Image 2:
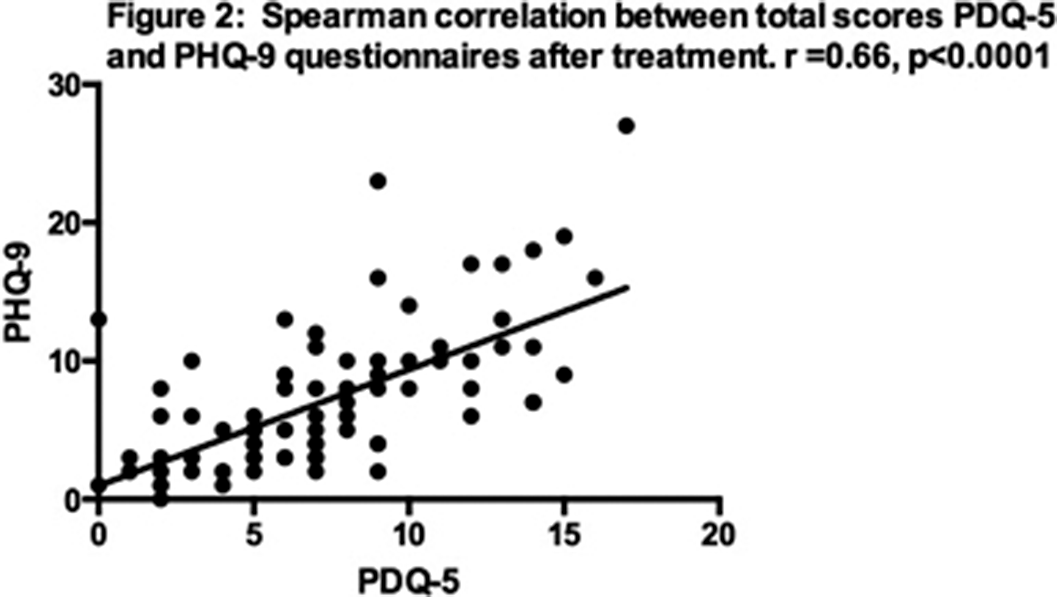
Significant improvements were found in the symptoms of depression, cognition and QOL in patients with MDD after treatment. Depression severity significantly inversely correlated with QOL and cognition of MDD patients.
None Declared
Comments
No Comments have been published for this article.