Published online by Cambridge University Press: 31 January 2020
Let X = (Xt)t≥0 be a stochastic process issued from  $x \in \mathbb{R}$
that admits a marginal stationary measure v, i.e. vPtf = vf for all t ≥ 0, where
$x \in \mathbb{R}$
that admits a marginal stationary measure v, i.e. vPtf = vf for all t ≥ 0, where 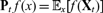 $\textbf{P}_t\,f(x)= \mathbb{E}_x[f(\textbf{X}_t)]$
. In this paper, we introduce the (resp. biorthogonal) spectral projections correlation functions which are expressed in terms of projections.” Also, update first published online date, if available. into the eigenspaces of Pt (resp. and of its adjoint in the weighted Hilbert space L2 (v)). We obtain closed-form expressions involving eigenvalues, the condition number and/or the angle between the projections in the following different situations: when X = X with X = (Xt)t ≥ 0 being a Markov process, X is the subordination of X in the sense of Bochner, and X is a non-Markovian process which is obtained by time-changing X with an inverse of a subordinator. It turns out that these spectral projections correlation functions have different expressions with respect to these classes of processes which enables to identify substantial and deep properties about their dynamics. This interesting fact can be used to design original statistical tests to make inferences, for example, about the path properties of the process (presence of jumps), distance from symmetry (self-adjoint or non-self-adjoint) and short-to-long-range dependence. To reveal the usefulness of our results, we apply them to a class of non-self-adjoint Markov semigroups studied in Patie and Savov (to appear, Mem. Amer. Math. Soc., 179p), and then time-change by subordinators and their inverses.
$\textbf{P}_t\,f(x)= \mathbb{E}_x[f(\textbf{X}_t)]$
. In this paper, we introduce the (resp. biorthogonal) spectral projections correlation functions which are expressed in terms of projections.” Also, update first published online date, if available. into the eigenspaces of Pt (resp. and of its adjoint in the weighted Hilbert space L2 (v)). We obtain closed-form expressions involving eigenvalues, the condition number and/or the angle between the projections in the following different situations: when X = X with X = (Xt)t ≥ 0 being a Markov process, X is the subordination of X in the sense of Bochner, and X is a non-Markovian process which is obtained by time-changing X with an inverse of a subordinator. It turns out that these spectral projections correlation functions have different expressions with respect to these classes of processes which enables to identify substantial and deep properties about their dynamics. This interesting fact can be used to design original statistical tests to make inferences, for example, about the path properties of the process (presence of jumps), distance from symmetry (self-adjoint or non-self-adjoint) and short-to-long-range dependence. To reveal the usefulness of our results, we apply them to a class of non-self-adjoint Markov semigroups studied in Patie and Savov (to appear, Mem. Amer. Math. Soc., 179p), and then time-change by subordinators and their inverses.