Article contents
Finite element approximation of kinetic dilutepolymer models with microscopic cut-off
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 15 April 2010
Abstract
We construct a Galerkin finite element method for the numerical approximation of weak solutions to a coupled microscopic-macroscopic bead-spring model that arises from the kinetic theory of dilute solutionsof polymeric liquids with noninteracting polymer chains. The model consists of the unsteady incompressible Navier–Stokes equations in a bounded domain Ω ⊂ $\mathbb{R}^d$ 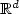 , d = 2 or 3, for the velocity andthe pressure of the fluid, with an elastic extra-stress tensor as right-hand side in the momentum equation. The extra-stress tensor stems from the random movement of the polymer chains and is defined through the associated probability density function that satisfies a Fokker–Planck type parabolic equation, crucial features of which are the presence of a centre-of-mass diffusion term and a cut-off function $\beta^L(\cdot) :=\min(\cdot,L)$
, d = 2 or 3, for the velocity andthe pressure of the fluid, with an elastic extra-stress tensor as right-hand side in the momentum equation. The extra-stress tensor stems from the random movement of the polymer chains and is defined through the associated probability density function that satisfies a Fokker–Planck type parabolic equation, crucial features of which are the presence of a centre-of-mass diffusion term and a cut-off function $\beta^L(\cdot) :=\min(\cdot,L)$ 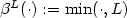 in the drag and convective terms, where L ≫ 1. We focus on finitely-extensible nonlinear elastic, FENE-type, dumbbell models. We perform a rigorous passage to the limit as the spatial and temporal discretization parameters tend to zero, and show that a (sub)sequence of these finite element approximations converges to a weak solution of this coupled Navier–Stokes–Fokker–Planck system. The passage to the limit is performed under minimal regularity assumptions on the data. Our arguments therefore also provide a new proof of global existence of weak solutions to Fokker–Planck–Navier–Stokes systems with centre-of-mass diffusion and microscopic cut-off. The convergence proof rests on several auxiliary technical results including the stability, in the Maxwellian-weighted H 1 norm, of the orthogonal projector in the Maxwellian-weighted L 2 inner product onto finite element spaces consisting of continuous piecewise linear functions.We establish optimal-order quasi-interpolation error bounds in the Maxwellian-weighted L 2 and H 1 norms,and prove a new elliptic regularity result in the Maxwellian-weighted H 2 norm.
in the drag and convective terms, where L ≫ 1. We focus on finitely-extensible nonlinear elastic, FENE-type, dumbbell models. We perform a rigorous passage to the limit as the spatial and temporal discretization parameters tend to zero, and show that a (sub)sequence of these finite element approximations converges to a weak solution of this coupled Navier–Stokes–Fokker–Planck system. The passage to the limit is performed under minimal regularity assumptions on the data. Our arguments therefore also provide a new proof of global existence of weak solutions to Fokker–Planck–Navier–Stokes systems with centre-of-mass diffusion and microscopic cut-off. The convergence proof rests on several auxiliary technical results including the stability, in the Maxwellian-weighted H 1 norm, of the orthogonal projector in the Maxwellian-weighted L 2 inner product onto finite element spaces consisting of continuous piecewise linear functions.We establish optimal-order quasi-interpolation error bounds in the Maxwellian-weighted L 2 and H 1 norms,and prove a new elliptic regularity result in the Maxwellian-weighted H 2 norm.
Keywords
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- ESAIM: Mathematical Modelling and Numerical Analysis , Volume 45 , Issue 1 , January 2011 , pp. 39 - 89
- Copyright
- © EDP Sciences, SMAI, 2010
References
- 10
- Cited by


