Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Cont, Rama
and
Voltchkova, Ekaterina
2003.
A Finite Difference Scheme for Option Pricing in Jump-diffusion and Exponential Levy Models.
SSRN Electronic Journal,
Cont, Rama
and
Voltchkova, Ekaterina
2005.
A Finite Difference Scheme for Option Pricing in Jump Diffusion and Exponential Lévy Models.
SIAM Journal on Numerical Analysis,
Vol. 43,
Issue. 4,
p.
1596.
Matache *, A.-M.
Nitsche, P.-A.
and
Schwab, C.
2005.
Wavelet Galerkin pricing of American options on Lévy driven assets.
Quantitative Finance,
Vol. 5,
Issue. 4,
p.
403.
Farkas, Walter
and
Schwab, Christoph
2006.
Anisotropic Stable Levy Copula Processes - Analysis and Numerical Pricing Methods.
SSRN Electronic Journal,
Matache, A. -M.
Schwab, C.
and
Wihler, T. P.
2006.
Linear Complexity Solution of Parabolic Integro-differential Equations.
Numerische Mathematik,
Vol. 104,
Issue. 1,
p.
69.
KUDRYAVTSEV, OLEG
and
LEVENDORSKIǏ, SERGEI
2006.
PRICING OF FIRST TOUCH DIGITALS UNDER NORMAL INVERSE GAUSSIAN PROCESSES.
International Journal of Theoretical and Applied Finance,
Vol. 09,
Issue. 06,
p.
915.
FARKAS, WALTER
REICH, NILS
and
SCHWAB, CHRISTOPH
2007.
ANISOTROPIC STABLE LEVY COPULA PROCESSES — ANALYTICAL AND NUMERICAL ASPECTS.
Mathematical Models and Methods in Applied Sciences,
Vol. 17,
Issue. 09,
p.
1405.
Winter, Christoph
and
Reich, Nils
2007.
Option pricing using multivariate Lévy processes.
PAMM,
Vol. 7,
Issue. 1,
p.
1081201.
Feng, Liming
Kovalov, Pavlo
Linetsky, Vadim
and
Marcozzi, Michael
2007.
Financial Engineering.
Vol. 15,
Issue. ,
p.
301.
Jakobsen, Espen R.
Karlsen, Kenneth H.
and
La Chioma, Claudia
2008.
Error estimates for approximate solutions to Bellman equations associated with controlled jump-diffusions.
Numerische Mathematik,
Vol. 110,
Issue. 2,
p.
221.
Benhamou, Eric
Gobet, Emmanuel
and
Miri, Mohammed
2008.
Smart Expansion and Fast Calibration for Jump Diffusion.
SSRN Electronic Journal,
Tangman, D.Y.
Gopaul, A.
and
Bhuruth, M.
2008.
Exponential time integration and Chebychev discretisation schemes for fast pricing of options.
Applied Numerical Mathematics,
Vol. 58,
Issue. 9,
p.
1309.
Mordecki, E.
Szepessy, A.
Tempone, R.
and
Zouraris, G. E.
2008.
Adaptive Weak Approximation of Diffusions with Jumps.
SIAM Journal on Numerical Analysis,
Vol. 46,
Issue. 4,
p.
1732.
Sachs, E.W.
and
Strauss, A.K.
2008.
Efficient solution of a partial integro-differential equation in finance.
Applied Numerical Mathematics,
Vol. 58,
Issue. 11,
p.
1687.
Toivanen, Jari
2008.
Numerical Valuation of European and American Options under Kou's Jump-Diffusion Model.
SIAM Journal on Scientific Computing,
Vol. 30,
Issue. 4,
p.
1949.
Kindermann, S.
Mayer, P.
Albrecher, H.
and
Engl, H.
2008.
Identification of the Local Speed Function in a Levy Model for Option Pricing.
Journal of Integral Equations and Applications,
Vol. 20,
Issue. 2,
Achdou, Yves
2008.
An Inverse Problem for a Parabolic Variational Inequality with an Integro-Differential Operator.
SIAM Journal on Control and Optimization,
Vol. 47,
Issue. 2,
p.
733.
Feng, Liming
and
Linetsky, Vadim
2008.
Pricing Options in Jump-Diffusion Models: An Extrapolation Approach.
Operations Research,
Vol. 56,
Issue. 2,
p.
304.
Clift, Simon S.
and
Forsyth, Peter A.
2008.
Numerical solution of two asset jump diffusion models for option valuation.
Applied Numerical Mathematics,
Vol. 58,
Issue. 6,
p.
743.
Tankov, Peter
and
Voltchkova, Ekaterina
2008.
Frontiers in Quantitative Finance.
p.
129.
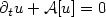 .This PIDE is localized tobounded domains and the error due to this localization isestimated. The localized PIDE is discretized by theθ-scheme in time and a wavelet Galerkin method with N degrees of freedom in log-price space. The dense matrix for ${\mathcal{A}}$
.This PIDE is localized tobounded domains and the error due to this localization isestimated. The localized PIDE is discretized by theθ-scheme in time and a wavelet Galerkin method with N degrees of freedom in log-price space. The dense matrix for ${\mathcal{A}}$ 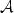 can be replaced by a sparse matrix in the wavelet basis, and the linear systemsin each implicit time step are solved approximativelywith GMRES in linear complexity. The total work of the algorithm for M time steps is bounded byO(MN(log(N))2) operations and O(Nlog(N)) memory.The deterministic algorithm gives optimal convergence rates (up to logarithmic terms) for the computed solutionin the same complexity as finite difference approximationsof the standard Black–Scholes equation.Computational examples for various Lévy price processes are presented.
can be replaced by a sparse matrix in the wavelet basis, and the linear systemsin each implicit time step are solved approximativelywith GMRES in linear complexity. The total work of the algorithm for M time steps is bounded byO(MN(log(N))2) operations and O(Nlog(N)) memory.The deterministic algorithm gives optimal convergence rates (up to logarithmic terms) for the computed solutionin the same complexity as finite difference approximationsof the standard Black–Scholes equation.Computational examples for various Lévy price processes are presented.