Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
ABDULLE, ASSYR
and
VILMART, GILLES
2012.
COUPLING HETEROGENEOUS MULTISCALE FEM WITH RUNGE–KUTTA METHODS FOR PARABOLIC HOMOGENIZATION PROBLEMS: A FULLY DISCRETE SPACETIME ANALYSIS.
Mathematical Models and Methods in Applied Sciences,
Vol. 22,
Issue. 06,
Gloria, Antoine
2013.
Fluctuation of Solutions to Linear Elliptic Equations with Noisy Diffusion Coefficients.
Communications in Partial Differential Equations,
Vol. 38,
Issue. 2,
p.
304.
Gloria, Antoine
and
Mourrat, Jean-Christophe
2013.
Quantitative version of the Kipnis–Varadhan theorem and Monte Carlo approximation of homogenized coefficients.
The Annals of Applied Probability,
Vol. 23,
Issue. 4,
Nolen, James
2014.
Normal approximation for a random elliptic equation.
Probability Theory and Related Fields,
Vol. 159,
Issue. 3-4,
p.
661.
Gloria, Antoine
Le Tallec, Patrick
and
Vidrascu, Marina
2014.
Foundation, analysis, and numerical investigation of a variational network-based model for rubber.
Continuum Mechanics and Thermodynamics,
Vol. 26,
Issue. 1,
p.
1.
Alexanderian, Alen
2015.
Expository Paper: A primer on homogenization of elliptic PDEs with stationary and ergodic random coefficient functions.
Rocky Mountain Journal of Mathematics,
Vol. 45,
Issue. 3,
Gloria, A.
Neukamm, S.
and
Otto, F.
2015.
Quantification of ergodicity in stochastic homogenization: optimal bounds via spectral gap on Glauber dynamics.
Inventiones mathematicae,
Vol. 199,
Issue. 2,
p.
455.
Gloria, Antoine
and
Habibi, Zakaria
2016.
Reduction in the Resonance Error in Numerical Homogenization II: Correctors and Extrapolation.
Foundations of Computational Mathematics,
Vol. 16,
Issue. 1,
p.
217.
Ben-Artzi, Jonathan
Marahrens, Daniel
and
Neukamm, Stefan
2017.
Moment bounds on the corrector of stochastic homogenization of non-symmetric elliptic finite difference equations.
Communications in Partial Differential Equations,
Vol. 42,
Issue. 2,
p.
179.
Fischer, Julian
2019.
The Choice of Representative Volumes in the Approximation of Effective Properties of Random Materials.
Archive for Rational Mechanics and Analysis,
Vol. 234,
Issue. 2,
p.
635.
Mourrat, J.-C.
2019.
Efficient Methods for the Estimation of Homogenized Coefficients.
Foundations of Computational Mathematics,
Vol. 19,
Issue. 2,
p.
435.
Gu, Chenlin
2020.
Uniform estimate of an iterative method for elliptic problems with rapidly oscillating coefficients.
Stochastics and Partial Differential Equations: Analysis and Computations,
Vol. 8,
Issue. 4,
p.
787.
Hannukainen, Antti
Mourrat, Jean-Christophe
and
Stoppels, Harmen T.
2021.
Computing homogenized coefficientsviamultiscale representation and hierarchical hybrid grids.
ESAIM: Mathematical Modelling and Numerical Analysis,
Vol. 55,
Issue. ,
p.
S149.
Armstrong, Scott
Hannukainen, Antti
Kuusi, Tuomo
and
Mourrat, Jean-Christophe
2021.
An iterative method for elliptic problems with rapidly oscillating coefficients.
ESAIM: Mathematical Modelling and Numerical Analysis,
Vol. 55,
Issue. 1,
p.
37.
Gu, Chenlin
2022.
An efficient algorithm for solving elliptic problems on percolation clusters.
The Annals of Applied Probability,
Vol. 32,
Issue. 4,
Lu, Jianfeng
Otto, Felix
and
Wang, Lihan
2024.
Optimal artificial boundary conditions based on second-order correctors for three dimensional random elliptic media.
Communications in Partial Differential Equations,
Vol. 49,
Issue. 7-8,
p.
609.
Hauck, Moritz
Mohr, Hannah
and
Peterseim, Daniel
2025.
A Simple Collocation-Type Approach to Numerical Stochastic Homogenization.
Multiscale Modeling & Simulation,
Vol. 23,
Issue. 1,
p.
374.
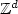 with independent and identically distributed conductivities on the associated edges.Recent results by Otto and the author quantify the error made by approximatingthe homogenized coefficient by the averaged energy of a regularizedcorrector (with parameter T) on some box of finite size L. In this article, we replace the regularizedcorrector (which is the solution of a problem posed on $\mathbb{Z}^d$
with independent and identically distributed conductivities on the associated edges.Recent results by Otto and the author quantify the error made by approximatingthe homogenized coefficient by the averaged energy of a regularizedcorrector (with parameter T) on some box of finite size L. In this article, we replace the regularizedcorrector (which is the solution of a problem posed on $\mathbb{Z}^d$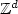 ) by some practically computable proxy on some box of size R ≥ L, and quantify the associated additional error.In order to improve the convergence, one may also consider N independentrealizations of the computable proxy, and take the empirical average of the associated approximate homogenized coefficients.A natural optimization problem consists in properly choosing T, R, L and N in order toreduce the error at given computational complexity.Our analysis is sharp and sheds some light on this question.In particular, we propose and analyze a numerical algorithm to approximate the homogenized coefficients, taking advantage of the (nearly) optimal scalings of the errorswe derive. The efficiency of the approach is illustrated by a numerical study in dimension 2.
) by some practically computable proxy on some box of size R ≥ L, and quantify the associated additional error.In order to improve the convergence, one may also consider N independentrealizations of the computable proxy, and take the empirical average of the associated approximate homogenized coefficients.A natural optimization problem consists in properly choosing T, R, L and N in order toreduce the error at given computational complexity.Our analysis is sharp and sheds some light on this question.In particular, we propose and analyze a numerical algorithm to approximate the homogenized coefficients, taking advantage of the (nearly) optimal scalings of the errorswe derive. The efficiency of the approach is illustrated by a numerical study in dimension 2.

