Article contents
Shy shadows of infinite-dimensional partially hyperbolic invariant sets
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 25 September 2017
Abstract
Let  ${\mathcal{R}}$ be a strongly compact
${\mathcal{R}}$ be a strongly compact 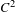 $C^{2}$ map defined in an open subset of an infinite-dimensional Banach space such that the image of its derivative
$C^{2}$ map defined in an open subset of an infinite-dimensional Banach space such that the image of its derivative  $D_{F}{\mathcal{R}}$ is dense for every
$D_{F}{\mathcal{R}}$ is dense for every  $F$. Let
$F$. Let 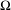 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FA}$ be a compact, forward invariant and partially hyperbolic set of
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FA}$ be a compact, forward invariant and partially hyperbolic set of 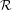 ${\mathcal{R}}$ such that
${\mathcal{R}}$ such that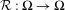 ${\mathcal{R}}:\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FA}\rightarrow \unicode[STIX]{x1D6FA}$ is onto. The
${\mathcal{R}}:\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FA}\rightarrow \unicode[STIX]{x1D6FA}$ is onto. The  $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FF}$-shadow
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FF}$-shadow  $W_{\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FF}}^{s}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FA})$ of
$W_{\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FF}}^{s}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FA})$ of 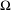 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FA}$ is the union of the sets
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FA}$ is the union of the sets 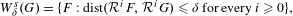 $$\begin{eqnarray}W_{\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FF}}^{s}(G)=\{F:\operatorname{dist}({\mathcal{R}}^{i}F,{\mathcal{R}}^{i}G)\leq \unicode[STIX]{x1D6FF}\text{for every }i\geq 0\},\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}W_{\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FF}}^{s}(G)=\{F:\operatorname{dist}({\mathcal{R}}^{i}F,{\mathcal{R}}^{i}G)\leq \unicode[STIX]{x1D6FF}\text{for every }i\geq 0\},\end{eqnarray}$$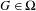 $G\in \unicode[STIX]{x1D6FA}$. Suppose that
$G\in \unicode[STIX]{x1D6FA}$. Suppose that 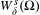 $W_{\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FF}}^{s}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FA})$ has transversal empty interior, that is, for every
$W_{\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FF}}^{s}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FA})$ has transversal empty interior, that is, for every  $C^{1+\text{Lip}}$
$C^{1+\text{Lip}}$ $n$-dimensional manifold
$n$-dimensional manifold  $M$ transversal to the distribution of dominated directions of
$M$ transversal to the distribution of dominated directions of 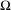 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FA}$ and sufficiently close to
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FA}$ and sufficiently close to 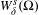 $W_{\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FF}}^{s}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FA})$ we have that
$W_{\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FF}}^{s}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FA})$ we have that 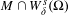 $M\cap W_{\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FF}}^{s}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FA})$ has empty interior in
$M\cap W_{\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FF}}^{s}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FA})$ has empty interior in 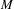 $M$. Here
$M$. Here  $n$ is the finite dimension of the strong unstable direction. We show that if
$n$ is the finite dimension of the strong unstable direction. We show that if 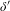 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FF}^{\prime }$ is small enough then
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FF}^{\prime }$ is small enough then 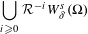 $$\begin{eqnarray}\mathop{\bigcup }_{i\geq 0}{\mathcal{R}}^{-i}W_{\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FF}^{\prime }}^{s}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FA})\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}\mathop{\bigcup }_{i\geq 0}{\mathcal{R}}^{-i}W_{\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FF}^{\prime }}^{s}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FA})\end{eqnarray}$$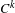 $C^{k}$-generic finite-dimensional curve inside the Banach space in a set of parameters with zero Lebesgue measure for every
$C^{k}$-generic finite-dimensional curve inside the Banach space in a set of parameters with zero Lebesgue measure for every 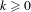 $k\geq 0$. This extends to infinite-dimensional dynamical systems previous studies on the Lebesgue measure of stable laminations of invariants sets.
$k\geq 0$. This extends to infinite-dimensional dynamical systems previous studies on the Lebesgue measure of stable laminations of invariants sets.
- Type
- Original Article
- Information
- Copyright
- © Cambridge University Press, 2017
References
- 1
- Cited by


