Article contents
Non-dense orbits on homogeneous spaces and applications to geometry and number theory
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 18 March 2021
Abstract
Let G be a Lie group, let 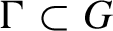 $\Gamma \subset G$
be a discrete subgroup, let
$\Gamma \subset G$
be a discrete subgroup, let 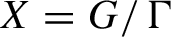 $X=G/\Gamma $
and let f be an affine map from X to itself. We give conditions on a submanifold Z of X that guarantee that the set of points
$X=G/\Gamma $
and let f be an affine map from X to itself. We give conditions on a submanifold Z of X that guarantee that the set of points 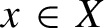 $x\in X$
with f-trajectories avoiding Z is hyperplane absolute winning (a property which implies full Hausdorff dimension and is stable under countable intersections). A similar result is proved for one-parameter actions on X. This has applications in constructing exceptional geodesics on locally symmetric spaces and in non-density of the set of values of certain functions at integer points.
$x\in X$
with f-trajectories avoiding Z is hyperplane absolute winning (a property which implies full Hausdorff dimension and is stable under countable intersections). A similar result is proved for one-parameter actions on X. This has applications in constructing exceptional geodesics on locally symmetric spaces and in non-density of the set of values of certain functions at integer points.
MSC classification
- Type
- Original Article
- Information
- Copyright
- © The Author(s), 2021. Published by Cambridge University Press
References
- 3
- Cited by



