Published online by Cambridge University Press: 26 February 2014
We first prove that topological fiber entropy potential in a relatively symbolic extension (topological joining with a subshift) of a topological dynamical system (which is a non-negative, non-decreasing, upper semicontinuous and subadditive potential 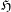 $\mathfrak{H}$) yields topological pressure equal to the topological entropy of the extended system. The terms occurring on the other side of the variational principle for pressure are equal to the extension entropies of the invariant measures. Thus the variational principle for pressure reduces to the usual variational principle (for entropy) applied to the extended system. Next we prove our main theorem saying that every non-negative, upper semicontinuous and subadditive potential
$\mathfrak{H}$) yields topological pressure equal to the topological entropy of the extended system. The terms occurring on the other side of the variational principle for pressure are equal to the extension entropies of the invariant measures. Thus the variational principle for pressure reduces to the usual variational principle (for entropy) applied to the extended system. Next we prove our main theorem saying that every non-negative, upper semicontinuous and subadditive potential 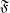 $\mathfrak{F}$ (we drop the monotonicity assumption) is ‘nearly equal’ to the fiber entropy potential H in some relatively symbolic extension of the system, in the sense that all terms occurring in the variational principle for pressure are the same for both potentials. This gives a new interpretation of all such potentials
$\mathfrak{F}$ (we drop the monotonicity assumption) is ‘nearly equal’ to the fiber entropy potential H in some relatively symbolic extension of the system, in the sense that all terms occurring in the variational principle for pressure are the same for both potentials. This gives a new interpretation of all such potentials 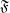 $\mathfrak{F}$ as a kind of additional information function enhancing the natural information arising from the dynamical system, and provides a new proof of the variational principle for pressure. At the end of the paper we provide examples showing that both assumptions, continuity and additivity, under which so-called lower pressure (defined with the help of spanning sets) equals the pressure, are essential, already in the class of non-negative, upper semicontinuous, subadditive potentials.
$\mathfrak{F}$ as a kind of additional information function enhancing the natural information arising from the dynamical system, and provides a new proof of the variational principle for pressure. At the end of the paper we provide examples showing that both assumptions, continuity and additivity, under which so-called lower pressure (defined with the help of spanning sets) equals the pressure, are essential, already in the class of non-negative, upper semicontinuous, subadditive potentials.