Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Kosloff, Zemer
2014.
On the K property for Maharam extensions of Bernoulli shifts and a question of Krengel.
Israel Journal of Mathematics,
Vol. 199,
Issue. 1,
p.
485.
Dooley, Anthony H.
Golodets, Valentyn Ya.
and
Zhang, Guohua
2014.
Sub-additive ergodic theorems for countable amenable groups.
Journal of Functional Analysis,
Vol. 267,
Issue. 5,
p.
1291.
Bowen, Lewis
and
Nevo, Amos
2015.
Amenable equivalence relations and the construction of ergodic averages for group actions.
Journal d'Analyse Mathématique,
Vol. 126,
Issue. 1,
p.
359.
TAO, TERENCE
2015.
FAILURE OF THE POINTWISE AND MAXIMAL ERGODIC THEOREMS FOR THE FREE GROUP.
Forum of Mathematics, Sigma,
Vol. 3,
Issue. ,
Houdayer, Cyril
and
Isono, Yusuke
2016.
Bi-Exact Groups, Strongly Ergodic Actions and Group Measure Space Type III Factors with No Central Sequence.
Communications in Mathematical Physics,
Vol. 348,
Issue. 3,
p.
991.
Vaes, Stefaan
and
Wahl, Jonas
2018.
Bernoulli actions of type III1 and L2-cohomology.
Geometric and Functional Analysis,
Vol. 28,
Issue. 2,
p.
518.
Huang, Xiaojun
Liu, Jinsong
and
Zhu, Changrong
2019.
Bowen topological entropy of subsets for amenable group actions.
Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications,
Vol. 472,
Issue. 2,
p.
1678.
Bernshteyn, Anton
2020.
Ergodic theorems for the shift action and pointwise versions of the Abért-Weiss theorem.
Israel Journal of Mathematics,
Vol. 235,
Issue. 1,
p.
255.
Nevo, Amos
and
Pogorzelski, Felix
2021.
The Shannon–McMillan–Breiman theorem beyond amenable groups.
Illinois Journal of Mathematics,
Vol. 65,
Issue. 4,
Wu, Haiyan
and
Li, Zhiming
2022.
An Alternative Definition of Topological Entropy for Amenable Group Actions.
Journal of Dynamical and Control Systems,
Vol. 28,
Issue. 2,
p.
333.
Bader, Uri
Boutonnet, Rémi
and
Houdayer, Cyril
2023.
Charmenability of higher rank arithmetic groups.
Annales Henri Lebesgue,
Vol. 6,
Issue. ,
p.
297.
Nevo, Amos
and
Pogorzelski, Felix
2024.
Shannon–McMillan–Breiman Theorem Along Almost Geodesics in Negatively Curved Groups.
Journal of Theoretical Probability,
Vol. 37,
Issue. 1,
p.
814.
 $_1$. We show that this class contains all irreducible lattices in connected semi-simple Lie groups without compact factors. We also establish similar results when the stable type is III
$_1$. We show that this class contains all irreducible lattices in connected semi-simple Lie groups without compact factors. We also establish similar results when the stable type is III $_\lambda $,
$_\lambda $, 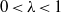 $0 \lt \lambda \lt 1$, under a suitable hypothesis. Our approach is based on the following two principles. First, we show that it is possible to generalize the ergodic theory of PMP actions of amenable groups to include PMP amenable equivalence relations. Secondly, we show that it is possible to reduce the proof of ergodic theorems for PMP actions of a general group to the proof of ergodic theorems in an associated PMP amenable equivalence relation, provided the group admits an amenable action with the properties stated above.
$0 \lt \lambda \lt 1$, under a suitable hypothesis. Our approach is based on the following two principles. First, we show that it is possible to generalize the ergodic theory of PMP actions of amenable groups to include PMP amenable equivalence relations. Secondly, we show that it is possible to reduce the proof of ergodic theorems for PMP actions of a general group to the proof of ergodic theorems in an associated PMP amenable equivalence relation, provided the group admits an amenable action with the properties stated above.