Article contents
On arithmetic progressions in non-periodic self-affine tilings
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 15 June 2021
Abstract
We study the repetition of patches in self-affine tilings in 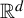 ${\mathbb {R}}^d$
. In particular, we study the existence and non-existence of arithmetic progressions. We first show that an arithmetic condition of the expansion map for a self-affine tiling implies the non-existence of certain one-dimensional arithmetic progressions. Next, we show that the existence of full-rank infinite arithmetic progressions, pure discrete dynamical spectrum, and limit-periodicity are all equivalent for a certain class of self-affine tilings. We finish by giving a complete picture for the existence or non-existence of full-rank infinite arithmetic progressions in the self-similar tilings in
${\mathbb {R}}^d$
. In particular, we study the existence and non-existence of arithmetic progressions. We first show that an arithmetic condition of the expansion map for a self-affine tiling implies the non-existence of certain one-dimensional arithmetic progressions. Next, we show that the existence of full-rank infinite arithmetic progressions, pure discrete dynamical spectrum, and limit-periodicity are all equivalent for a certain class of self-affine tilings. We finish by giving a complete picture for the existence or non-existence of full-rank infinite arithmetic progressions in the self-similar tilings in 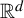 ${\mathbb {R}}^d$
.
${\mathbb {R}}^d$
.
MSC classification
- Type
- Original Article
- Information
- Copyright
- © The Author(s), 2021. Published by Cambridge University Press
References
- 2
- Cited by



