Published online by Cambridge University Press: 10 November 2014
In this article we will extend ‘the weak mixing theorem’ for certain locally compact Polish groups (Moore groups and minimally weakly mixing groups). In addition, we will show that the Gaussian action associated with the infinite-dimensional irreducible representation of the continuous Heisenberg group, 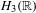 $H_{3}(\mathbb{R})$, is weakly mixing but not mildly mixing.
$H_{3}(\mathbb{R})$, is weakly mixing but not mildly mixing.